Comparative Effects of Allulose, Fructose, and Glucose on the Small Intestine
- PMID: 35956407
- PMCID: PMC9370476
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14153230
Comparative Effects of Allulose, Fructose, and Glucose on the Small Intestine
Abstract
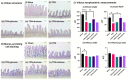
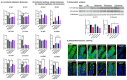
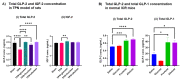
Despite numerous studies on the health benefits of the rare sugar allulose, its effects on intestinal mucosal morphology and function are unclear. We therefore first determined its acute effects on the small intestinal transcriptome using DNA microarray analysis following intestinal allulose, fructose and glucose perfusion in rats. Expression levels of about 8-fold more genes were altered by allulose compared to fructose and glucose perfusion, suggesting a much greater impact on the intestinal transcriptome. Subsequent pathway analysis indicated that nutrient transport, metabolism, and digestive system development were markedly upregulated, suggesting allulose may acutely stimulate these functions. We then evaluated whether allulose can restore rat small intestinal structure and function when ingested orally following total parenteral nutrition (TPN). We also monitored allulose effects on blood levels of glucagon-like peptides (GLP) 1 and 2 in TPN rats and normal mice. Expression levels of fatty acid binding and gut barrier proteins were reduced by TPN but rescued by allulose ingestion, and paralleled GLP-2 secretion potentially acting as the mechanism mediating the rescue effect. Thus, allulose can potentially enhance disrupted gut mucosal barriers as it can more extensively modulate the intestinal transcriptome relative to glucose and fructose considered risk factors of metabolic disease.
Keywords: allulose; fructose; glucose; intestinal barrier; nutrient digestion and absorption; small intestinal function; small intestine.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was partly supported by the funding from Matsutani Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. Purified D-allulose was supplied by the company in accordance with the Material Transfer Agreement between Takuji Suzuki and Matsutani Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. The funders excluding Matsutani Chemical Industry Co., Ltd. had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. The other authors have no competing interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Oshima: H., Kimura I., Izumori K. Psicose contents in various food products and its origin. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2006;12:137–143. doi: 10.3136/fstr.12.137. - DOI
-
- Hossain M.A., Kitagaki S., Nakano D., Nishiyama A., Funamoto Y., Matsunaga T., Tsukamoto I., Yamaguchi F., Kamitori K., Dong Y., et al. Rare sugar D-psicose improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in type 2 diabetes Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011;405:7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.091. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hossain A., Yamaguchi F., Matsunaga T., Hirata Y., Kamitori K., Dong Y., Sui L., Tsukamoto I., Ueno M., Tokuda M. Rare sugar D-psicose protects pancreas beta-islets and thus improves insulin resistance in OLETF rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012;425:717–723. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.135. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hossain A., Yamaguchi F., Hirose K., Matsunaga T., Sui L., Hirata Y., Noguchi C., Katagi A., Kamitori K., Dong Y., et al. Rare sugar D-psicose prevents progression and development of diabetes in T2DM model Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015;9:525–535. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S71289. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2014/Hoansha Foundation
- 2019-2020/Matsutani Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.
- Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B), grant number 23700909/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C), grant number 18K11123/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research, grant number 21K19698/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

