Marker-Trait Associations for Total Carotenoid Content and Individual Carotenoids in Durum Wheat Identified by Genome-Wide Association Analysis
- PMID: 35956543
- PMCID: PMC9370666
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11152065
Marker-Trait Associations for Total Carotenoid Content and Individual Carotenoids in Durum Wheat Identified by Genome-Wide Association Analysis
Abstract
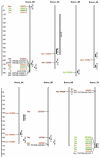
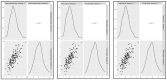
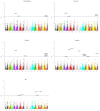
Yellow pigment content is one of the main traits considered for grain quality in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L.). The yellow color is mostly determined by carotenoid pigments, lutein being the most abundant in wheat endosperm, although zeaxanthin, α-carotene and β-carotene are present in minor quantities. Due to the importance of carotenoids in human health and grain quality, modifying the carotenoid content and profile has been a classic target. Landraces are then a potential source for the variability needed for wheat breeding. In this work, 158 accessions of the Spanish durum wheat collection were characterized for carotenoid content and profile and genotyped using the DArTSeq platform for association analysis. A total of 28 marker-trait associations were identified and their co-location with previously described QTLs and candidate genes was studied. The results obtained confirm the importance of the widely described QTL in 7B and validate the QTL regions recently identified by haplotype analysis for the semolina pigment. Additionally, copies of the Zds and Psy genes on chromosomes 7B and 5B, respectively, may have a putative role in determining zeaxanthin content. Finally, genes for the methylerythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) and isopentenyl diphosphate (IPPI) carotenoid precursor pathways were revealed as additional sources of untapped variation for carotenoid improvement.
Keywords: GWAS; Triticum turgidum; grain quality; landraces.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Genetic approaches to exploit landraces for improvement of Triticum turgidum ssp. durum in the age of climate change.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 27;14:1101271. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1101271. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36778704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Durum Wheat (Triticum durum L.) Landraces Reveal Potential for the Improvement of Grain Carotenoid Esterification in Breeding Programs.Foods. 2021 Apr 2;10(4):757. doi: 10.3390/foods10040757. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33918139 Free PMC article.
-
Carotenoid Pigment Content in Durum Wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var durum): An Overview of Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Nov 7;10:1347. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01347. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31787991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of QTL and association of a phytoene synthase gene with endosperm colour in durum wheat.Theor Appl Genet. 2007 Feb;114(3):525-37. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0453-5. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Theor Appl Genet. 2007. PMID: 17131106
-
Allelic variation at Psy1-A1 and association with yellow pigment in durum wheat grain.Theor Appl Genet. 2009 May;118(8):1539-48. doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1001-x. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Theor Appl Genet. 2009. PMID: 19319504
Cited by
-
Towards carotenoid biofortification in wheat: identification of XAT-7A1, a multicopy tandem gene responsible for carotenoid esterification in durum wheat.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Sep 6;23(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04431-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37674126 Free PMC article.
-
Bread Wheat Biofortification for Grain Carotenoid Content by Inter-Specific Breeding.Foods. 2023 Mar 23;12(7):1365. doi: 10.3390/foods12071365. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37048186 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic approaches to exploit landraces for improvement of Triticum turgidum ssp. durum in the age of climate change.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 27;14:1101271. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1101271. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36778704 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada Canada: Outlook for Principal Field Crops. Mar 1, 2022. [(accessed on 5 July 2022)]. Available online: https://agriculture.canada.ca/en/canadas-agriculture-sectors/crops/canad....
-
- Eurostat Eurostat Database: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/main/data/database. [(accessed on 5 July 2022)]. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat.
-
- Colasuonno P., Marcotuli I., Blanco A., Maccaferri M., Condorelli G.E., Tuberosa R., Parada R., de Camargo A.C., Schwember A.R., Gadaleta A. Carotenoid pigment content in durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L. var durum): An overview of quantitative trait loci and candidate genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2019;10:1347. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01347. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ficco D.B.M., Mastrangelo A.M., Trono D., Borrelli G.M., De Vita P., Fares C., Beleggia R., Platani C., Papa R. The colours of durum wheat: A review. Crop Pasture Sci. 2014;65:1–15. doi: 10.1071/CP13293. - DOI
-
- Rodríguez-Suárez C., Giménez M.J., Atienza S.G. Progress and perspectives for carotenoid accumulation in selected Triticeae species. Crop Pasture Sci. 2010;61:743. doi: 10.1071/CP10025. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

