In Vitro Evaluation of Kaempferol-Loaded Hydrogel as pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems
- PMID: 35956719
- PMCID: PMC9370943
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14153205
In Vitro Evaluation of Kaempferol-Loaded Hydrogel as pH-Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
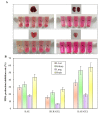
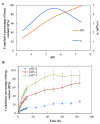
The purpose of this study was to prepare and evaluate kaempferol-loaded carbopol polymer (acrylic acid) hydrogel, investigate its antioxidant activity in vitro, and compare the effects on drug release under different pH conditions. Drug release studies were conducted in three different pH media (pH 3.4, 5.4, and 7.4). The kaempferol-loaded hydrogel was prepared by using carbopol 934 as the hydrogel matrix. The morphology and viscosity of the preparation were tested to understand the fluidity of the hydrogel. The antioxidant activity of the preparation was studied by scavenging hydrogen peroxide and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrilhidrazil (DPPH) radicals in vitro and inhibiting the production of malondialdehyde in mouse tissues. The results showed that kaempferol and its preparations had high antioxidant activity. In vitro release studies showed that the drug release at pH 3.4, 5.4, and 7.4 was 27.32 ± 3.49%, 70.89 ± 8.91%, and 87.9 ± 10.13%, respectively. Kaempferol-loaded carbopol hydrogel displayed greater swelling and drug release at higher pH values (pH 7.4).
Keywords: antioxidation; carbopol 934; different pH; drug release; kaempferol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Development of novel pH-sensitive nanoparticles loaded hydrogel for transdermal drug delivery.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019 Apr;45(4):629-641. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2019.1569031. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019. PMID: 30633578
-
Formulation and rheological evaluation of ethosome-loaded carbopol hydrogel for transdermal application.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016 Aug;42(8):1315-24. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2015.1132227. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26727599
-
Formulation and In-Vitro Characterization of pH-Responsive Semi-Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels for Controlled Release of Ketorolac Tromethamine.Gels. 2021 Oct 13;7(4):167. doi: 10.3390/gels7040167. Gels. 2021. PMID: 34698162 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Irradiated chitosan based injectable hydrogels for controlled release of drug (Montelukast sodium).Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Jul 15;114:890-897. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.107. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29458102
-
Radiation Synthesis of Poly(Starch/Acrylic acid) pH Sensitive Hydrogel for Rutin Controlled Release.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Nov;92:957-964. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.079. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 27471091
Cited by
-
Study on the Antioxidant Effect of Shikonin-Loaded β-Cyclodextrin Forming Host-Guest Complexes That Prevent Skin from Photoaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 14;24(20):15177. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015177. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894857 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents in the Atopic Dermatitis Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 15;17(2):261. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020261. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Graphene-Based Nanocomposite Gels as a Promising Wound Healing Biomaterial.Gels. 2022 Dec 28;9(1):22. doi: 10.3390/gels9010022. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36661790 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization, Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity of Hydrogels Containing Propolis Extract as an Alternative Treatment in Wound Healing.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;17(5):575. doi: 10.3390/ph17050575. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794145 Free PMC article.
-
From Plants to Wound Dressing and Transdermal Delivery of Bioactive Compounds.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 16;12(14):2661. doi: 10.3390/plants12142661. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

