Biochemical Characterization and In Vitro Digestibility of Protein Isolates from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) By-Products for Salmonid Feed Applications
- PMID: 35956747
- PMCID: PMC9369619
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154794
Biochemical Characterization and In Vitro Digestibility of Protein Isolates from Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) By-Products for Salmonid Feed Applications
Abstract
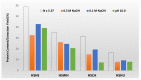
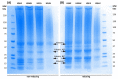
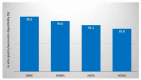
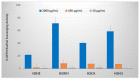
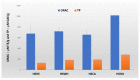
Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) processing by-products (hemp cake and hemp seed hulls) were studied for their protein content, extraction of protein isolates (PIs), and their in vitro protein digestibility (IVPD). Crude protein contents of hemp cake and hemp seed hulls were 30.4% and 8.6%, respectively, calculated based on generalized N-to-P conversion factor (N × 5.37). Extraction efficiency of PIs from defatted biomass ranged from 56.0 to 67.7% with alkaline extraction (0.1 M NaOH) followed by isoelectric precipitation (1.0 M HCl). Nitrogen analysis suggested that the total protein contents of PIs extracted using three different alkaline conditions (0.5 M, 0.1 M, and pH 10.0 with NaOH) were >69.7%. The hemp by-product PIs contained all essential amino acids (EAAs) required for fish with leucine, valine, and phenylalanine belonging to the five dominant amino acids. Overall, glutamate was the dominant non-EAA followed by aspartate. Coomassie staining of an SDS-PAGE gel revealed strong presence of the storage protein edestin. High IVPD of >88% was observed for PIs extracted from hemp seeds and by-products when evaluated using a two-phase in vitro gastric/pancreatic protein digestibility assay. PIs extracted from by-products were further tested for their antioxidant activities. The tested PIs showed dose-dependent DPPH radical scavenging activity and possessed strong ORAC values > 650 μM TE/g.
Keywords: Cannabis sativa; amino acids; antioxidant; hemp by-products; hemp cake; hemp hulls; hemp seed; in vitro digestibility; protein isolate; total phenolic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed oil press-cake and decaffeinated green tea leaves (Camellia sinensis) on functional characteristics of gluten-free crackers.J Food Sci. 2014 Mar;79(3):C318-25. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12370. Epub 2014 Feb 13. J Food Sci. 2014. PMID: 24527987
-
Production, digestibility and allergenicity of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolates.Food Res Int. 2019 Jan;115:562-571. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.09.017. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30599980
-
Triacylglycerols and Other Lipids Profiling of Hemp By-Products.Molecules. 2022 Apr 5;27(7):2339. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072339. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408737 Free PMC article.
-
Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.) as a Valuable Source of Natural Ingredients for Functional Foods-A Review.Molecules. 2024 May 1;29(9):2097. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092097. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds from Cannabis sativa Seeds: A Review Focused on Omics-Based Investigations.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 29;26(11):5219. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115219. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Polar Lipids in Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) By-Products by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry.Molecules. 2022 Sep 9;27(18):5856. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185856. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144592 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Quality, Chemical, and Functional Characteristics of Hemp (Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa) Protein Isolate.Plants (Basel). 2022 Oct 24;11(21):2825. doi: 10.3390/plants11212825. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36365277 Free PMC article.
-
Hemp: A Sustainable Plant with High Industrial Value in Food Processing.Foods. 2023 Feb 2;12(3):651. doi: 10.3390/foods12030651. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36766179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in Biological Ammonia Production.BioTech (Basel). 2023 May 19;12(2):41. doi: 10.3390/biotech12020041. BioTech (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37218758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising Dietary Supplements with Potential Senotherapeutic Effects: Aqueous Extracts from Enzymatically Hydrolysed Hemp Seed Cake Flour and Hemp Seed Protein Concentrate.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 15;14(6):734. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060734. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kobayshi M., Msangi S., Batka M., Vannccini S., Dey M.D., Anderson J.L. Fish to 2030: The role and opportunity for aquaculture. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2015;19:282–300. doi: 10.1080/13657305.2015.994240. - DOI
-
- Cottrell R.S., Blanchard J.L., Halpern B.S., Metian M., Froehlich H.E. Global adoption of novel aquaculture feeds could substantially reduce forage fish demand by 2030. Nat. Food. 2020;1:302–308. doi: 10.1038/s43016-020-0078-x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

