Small Molecular Drug Screening Based on Clinical Therapeutic Effect
- PMID: 35956770
- PMCID: PMC9369618
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154807
Small Molecular Drug Screening Based on Clinical Therapeutic Effect
Abstract
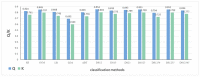
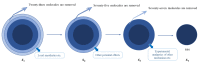
Virtual screening can significantly save experimental time and costs for early drug discovery. Drug multi-classification can speed up virtual screening and quickly predict the most likely class for a drug. In this study, 1019 drug molecules with actual therapeutic effects are collected from multiple databases and documents, and molecular sets are grouped according to therapeutic effect and mechanism of action. Molecular descriptors and molecular fingerprints are obtained through SMILES to quantify molecular structures. After using the Kennard-Stone method to divide the data set, a better combination can be obtained by comparing the combined results of five classification algorithms and a fusion method. Furthermore, for a specific data set, the model with the best performance is used to predict the validation data set. The test set shows that prediction accuracy can reach 0.862 and kappa coefficient can reach 0.808. The highest classification accuracy of the validation set is 0.873. The more reliable molecular set has been found, which could be used to predict potential attributes of unknown drug compounds and even to discover new use for old drugs. We hope this research can provide a reference for virtual screening of multiple classes of drugs at the same time in the future.
Keywords: Dempster–Shafer theory; Kennard–Stone division; molecular descriptor; molecular fingerprint.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Molecular fingerprint similarity search in virtual screening.Methods. 2015 Jan;71:58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.08.005. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Methods. 2015. PMID: 25132639 Review.
-
ADMET evaluation in drug discovery. 13. Development of in silico prediction models for P-glycoprotein substrates.Mol Pharm. 2014 Mar 3;11(3):716-26. doi: 10.1021/mp400450m. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Mol Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24499501
-
Comparison of topological descriptors for similarity-based virtual screening using multiple bioactive reference structures.Org Biomol Chem. 2004 Nov 21;2(22):3256-66. doi: 10.1039/B409865J. Epub 2004 Sep 29. Org Biomol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15534703
-
How diverse are diversity assessment methods? A comparative analysis and benchmarking of molecular descriptor space.J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Jan 27;54(1):230-42. doi: 10.1021/ci400469u. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J Chem Inf Model. 2014. PMID: 24289493
-
A review of ligand-based virtual screening web tools and screening algorithms in large molecular databases in the age of big data.Future Med Chem. 2018 Nov;10(22):2641-2658. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0076. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Future Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30499744 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

