Aliskiren Hemifumarate Proliposomes for Improved Oral Drug Delivery: Formulation Development, In Vitro and In Vivo Permeability Testing
- PMID: 35956779
- PMCID: PMC9369865
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154828
Aliskiren Hemifumarate Proliposomes for Improved Oral Drug Delivery: Formulation Development, In Vitro and In Vivo Permeability Testing
Abstract
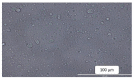
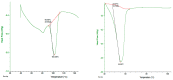
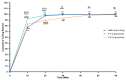
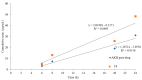
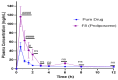
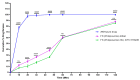
The objective of this study was to develop proliposomal formulations for a poorly bioavailable drug, aliskiren hemifumarate (AKH). A solvent evaporation method was used to prepare proliposomes using different lipids. The lipids of selection were soy phosphatidylcholine (SPC), dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC), and dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol sodium (DMPG Na), stearylamine, and cholesterol in various ratios. Proliposomes were evaluated for particle size, zeta potential, in vitro drug release, in vitro permeability, and in vivo pharmacokinetics upon hydration with aqueous phase. In vitro drug release studies were conducted in 0.01 N hydrochloric acid using USP type II dissolution apparatus. Parallel artificial membrane permeation assay (PAMPA) and Caco-2 cell line models were used to study the in vitro drug permeation. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were used to conduct in vivo pharmacokinetic studies. Among different formulations, proliposomes with drug/DMPC/cholesterol/stearylamine in the ratio of 1:5:0.025:0.050 (w/w/w/w) demonstrated the desired particle size, higher zeta potential, and higher encapsulation efficiency. The PAMPA and Caco-2 cell line experiments showed a significantly higher permeability of AKH with proliposomes as compared to pure AKH. In animal studies, the optimized formulation of proliposomes showed significant improvement in the rate and extent of absorption of AKH. Specifically, following a single oral administration, the relative bioavailability of AKH proliposome formulation was 230% when compared to pure AKH suspension.
Keywords: Caco-2; PAMPA; aliskiren hemifumarate; pharmacokinetic studies; proliposomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Understanding a Heart Attack—What Just Happened. [(accessed on 11 June 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
-
- Heart Attack Related Stories—Your Road to Recovery. [(accessed on 12 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure.
-
- Aliskiren is a Direct Renin Inhibitor Used to Manage Hypertension. [(accessed on 10 May 2020)]. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09026.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

