Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Environment Using Terephthaldehyde Based on Schiff Base: Gravimetric, Thermodynamic, and Computational Studies
- PMID: 35956814
- PMCID: PMC9370009
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154857
Corrosion Inhibition of Mild Steel in Hydrochloric Acid Environment Using Terephthaldehyde Based on Schiff Base: Gravimetric, Thermodynamic, and Computational Studies
Abstract
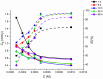
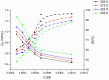
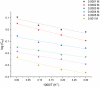
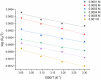
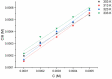
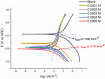
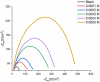
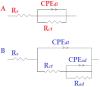
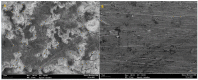
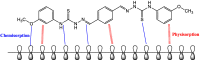
Using traditional weight-loss tests, as well as different electrochemical techniques (potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy), we investigated the corrosion-inhibition performance of 2,2′-(1,4-phenylenebis(methanylylidene)) bis(N-(3-methoxyphenyl) hydrazinecarbothioamide) (PMBMH) as an inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M hydrochloric acid solution. The maximum protection efficacy of 0.0005 M of PMBMH was 95%. Due to the creation of a protective adsorption layer instead of the adsorbed H2O molecules and acidic chloride ions, the existence of the investigated inhibitor reduced the corrosion rate and increased the inhibitory efficacy. The inhibition efficiency increased as the inhibitor concentration increased, but it decreased as the temperature increased. The PMBMH adsorption mode followed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm, with high adsorption-inhibition activity. Furthermore, the value of the ∆Gadso indicated that PMBMH contributed to the physical and chemical adsorption onto the mild-steel surface. Moreover, density functional theory (DFT) helped in the calculation of the quantum chemical parameters for finding the correlation between the inhibition activity and the molecular structure. The experimental and theoretical findings in this investigation are in good agreement.
Keywords: DFT; EIS; Schiff base; corrosion inhibitor; terephthaldehyde; weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
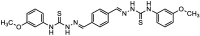

Similar articles
-
Electrochemical and quantum chemical studies of N,N'-bis(4-hydroxybenzaldehyde)-2,2-dimethylpropandiimine Schiff base as corrosion inhibitor for low carbon steel in HCl solution.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2013;48(13):1628-41. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2013.815094. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2013. PMID: 23947700
-
Inhibitory effect of xanthan gum and synergistic surfactant additives for mild steel corrosion in 1M HCl.Carbohydr Polym. 2016 Jan 20;136:384-93. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.09.027. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Carbohydr Polym. 2016. PMID: 26572368
-
Corrosion inhibition of mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution by the expired Ampicillin drug.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 25;13(1):6724. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-33519-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37185806 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation of Imine Metal Chelates as Corrosion Inhibitors at Different Media: A Collective Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 19;23(16):9360. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169360. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in ionic liquid-based corrosion inhibitors for sustainable protection strategies: from experimental to computational insights.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Nov;333:103303. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103303. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 39303355 Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation of Bis-Thiophene Schiff Alkali-Copper Metal Complex for Metal Corrosion Inhibition.Materials (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;16(8):3214. doi: 10.3390/ma16083214. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37110049 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental and Quantum Chemical Investigations on the Anticorrosion Efficiency of a Nicotinehydrazide Derivative for Mild Steel in HCl.Molecules. 2022 Sep 23;27(19):6254. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196254. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234791 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive evaluation of 5-imino-1,2,4-dithiazolidine-3-thione as a corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 26;15(1):10349. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95104-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40133609 Free PMC article.
-
Isatin Schiff base is an effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution: gravimetrical, electrochemical, and computational investigation.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 22;12(1):17773. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22611-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36273029 Free PMC article.
-
Melamine-isatin tris Schiff base as an efficient corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 0.5 molar hydrochloric acid solution: weight loss, electrochemical and surface studies.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 26;13(28):19301-19311. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00357d. eCollection 2023 Jun 22. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37377871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yadav M., Yadav P., Sharma U. Substituted imidazoles as corrosion inhibitors for N80 steel in hydrochloric acid. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2013;20:363–370.
-
- Zarrok H., Assouag M., Zarrouk A., Oudda H., Hallaoui A., Touzani R., Allali M., Hammouti B., El Hezzat M., Bouachrine M. Quantum chemical study on the corrosion inhibition of some bipyrazoles. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2015;6:1853–1860.
-
- Gece G. The use of quantum chemical methods in corrosion inhibitor studies. Corros. Sci. 2008;50:2981–2992. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2008.08.043. - DOI
-
- Obot I.B., Macdonald D.D., Gasem Z.M. Density functional theory (DFT) as a powerful tool for designing new organic corrosion inhibitors. Part 1: An overview. Corros. Sci. 2015;99:1–30. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.01.037. - DOI
-
- Camacho-Mendoza R.L., Gutiérrez-Moreno E., Guzmán-Percástegui E., Aquino-Torres E., Cruz-Borbolla J., Rodríguez-Ávila J.A., Alvarado-Rodríguez J.G., Olvera-Neria O., Thangarasu P., Medina-Franco J.L. Density Functional Theory and Electrochemical Studies: Structure-Efficiency Relationship on Corrosion Inhibition. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015;55:2391–2402. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00385. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

