Discovery of New Inhibitors of eEF2K from Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on In Silico Screening and In Vitro Experimental Validation
- PMID: 35956836
- PMCID: PMC9369671
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154886
Discovery of New Inhibitors of eEF2K from Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on In Silico Screening and In Vitro Experimental Validation
Abstract
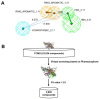
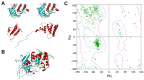
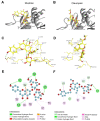
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K) is a highly conserved α kinase and is increasingly considered as an attractive therapeutic target for cancer as well as other diseases. However, so far, no selective and potent inhibitors of eEF2K have been identified. In this study, pharmacophore screening, homology modeling, and molecular docking methods were adopted to screen novel inhibitor hits of eEF2K from the traditional Chinese medicine database (TCMD), and then cytotoxicity assay and western blotting were performed to verify the validity of the screen. Resultantly, after two steps of screening, a total of 1077 chemicals were obtained as inhibitor hits for eEF2K from all 23,034 compounds in TCMD. Then, to verify the validity, the top 10 purchasable chemicals were further analyzed. Afterward, Oleuropein and Rhoifolin, two reported antitumor chemicals, were found to have low cytotoxicity but potent inhibitory effects on eEF2K activity. Finally, molecular dynamics simulation, pharmacokinetic and toxicological analyses were conducted to evaluate the property and potential of Oleuropein and Rhoifolin to be drugs. Together, by integrating in silico screening and in vitro biochemical studies, Oleuropein and Rhoifolin were revealed as novel eEF2K inhibitors, which will shed new lights for eEF2K-targeting drug development and anticancer therapy.
Keywords: anticancer; eEF2K inhibitors; molecular docking; pharmacophore screening; traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of polo-like kinase 1/eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (PLK1/EEF2K) dual inhibitors for regulating breast cancer cells apoptosis and autophagy.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 20;144:517-528. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.12.046. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29288948
-
Novel inhibitors of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase: In silico, synthesis and in vitro studies.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Nov;116:105296. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105296. Epub 2021 Aug 23. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34488125
-
Targeting eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF2K) with small-molecule inhibitors for cancer therapy.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Oct;29(10):104155. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104155. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 39214495 Review.
-
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase as a drug target in cancer, and in cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Mar;37(3):285-94. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.123. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 26806303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationship of a focused library of β-phenylalanine derivatives as novel eEF2K inhibitors with apoptosis-inducing mechanisms in breast cancer.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:402-418. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.065. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29202403
Cited by
-
Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Asiaticoside on Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism, and Gut Microbiota in Yellow-Feathered Chickens.Animals (Basel). 2023 Aug 17;13(16):2653. doi: 10.3390/ani13162653. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627444 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of skeletal carbohydrate-response element binding protein (ChREBP)-mediated de novo lipogenesis increases intramuscular fat content in chickens.Anim Nutr. 2024 Apr 16;18:107-118. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.04.006. eCollection 2024 Sep. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39091296 Free PMC article.
-
East meets West: The winning combination against BRAF V600E metastatic colorectal cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2025 May 24;16(5):102223. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v16.i5.102223. World J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40503402 Free PMC article.
-
eEF2K Inhibitor Design: The Progression of Exemplary Structure-Based Drug Design.Molecules. 2023 Jan 21;28(3):1095. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031095. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770760 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

