Ultrasonic Extraction of 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline (2AP) from Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. Using Ethanol as Solvent
- PMID: 35956856
- PMCID: PMC9370269
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154906
Ultrasonic Extraction of 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline (2AP) from Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. Using Ethanol as Solvent
Abstract
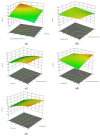
2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP) is the compound that gives out the typical aroma and flavour of pandan leaves (Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb.). This research incorporates ultrasonic extraction to extract the aromatic compound in pandan leaves. The parameters varied in this study are the extraction time, sonicator amplitude, concentration of solvent and the mass of pandan leaves. The experiment was conducted using a central composite design (CCD) model generated by the response surface methodology (RSM). From the extraction process, it can be deduced that the effect of leaves' mass is comparably higher than other parameters, while sonicator amplitude gives the most negligible impact on the process. The obtained p-value was 0.0014, which was less than 0.05. The high R-squared 0.9603 and adjusted R-squared 0.8809 indicate the model is well agreed with the actual data. The optimal control variables of ultrasonic extraction of 2AP are at an extraction time of 20 min, 60% of solvent concentration, amplitude of 25% and 12.5 g of pandan leaves, which produced 60.51% of yield of the extract and 1.43 ppm of 2AP. It is found that the mass of pandan leaves and the concentration of solvent have a significant impact on the extraction process of 2AP.
Keywords: 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline (2AP); RSM; pandan leaves; solvent; ultrasonic extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Routray W., Rayaguru K. Chemical Constituents and Post-Harvest Prospects of Pandanus amaryllifolius Leaves: A Review. Food Rev. Int. 2014;26:51–54.
-
- Ngadi N., Yahya N.Y. Extraction of 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline (2AP) in Pandan Leaves (Pandanus Amaryllifolius Roxb.) Via Solvent Extraction Method: Effect of Solvent. J. Teknol. 2014;67:51–54. doi: 10.11113/jt.v67.2735. - DOI
-
- Wongpornchai S. Handbook of Herbs and Spices. Volume 3. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, UK: 2006. Pandan Wangi; p. 458.
-
- Rosello-Soto E., Koubaa M., Moubarik A., Lopes R.P., Saraiva J.A., Boussetta N., Grimi N., Braba F.J. Emerging opportunities for the effective valorization of wastes and by-products generated during olive oil production process: Non-conventional methods for the recovery of high-added value compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015;45:296–310. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2015.07.003. - DOI
-
- Kusters K.A., Pratsinis S.E., Thoma S.G., Smith D.M. Energy—Size reduction laws for ultrasonic fragmentation. Powder Technol. 1994;80:253–263. doi: 10.1016/0032-5910(94)02852-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

