Metalloporphyrin Metal-Organic Frameworks: Eminent Synthetic Strategies and Recent Practical Exploitations
- PMID: 35956867
- PMCID: PMC9369971
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154917
Metalloporphyrin Metal-Organic Frameworks: Eminent Synthetic Strategies and Recent Practical Exploitations
Abstract
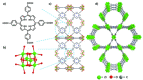
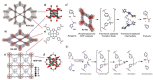
The emergence of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) in recent years has stimulated the interest of scientists working in this area as one of the most applicable archetypes of three-dimensional structures that can be used as promising materials in several applications including but not limited to (photo-)catalysis, sensing, separation, adsorption, biological and electrochemical efficiencies and so on. Not only do MOFs have their own specific versatile structures, tunable cavities, and remarkably high surface areas, but they also present many alternative procedures to overcome emerging obstacles. Since the discovery of such highly effective materials, they have been employed for multiple uses; additionally, the efforts towards the synthesis of MOFs with specific properties based on planned (template) synthesis have led to the construction of several promising types of MOFs possessing large biological or bioinspired ligands. Specifically, metalloporphyrin-based MOFs have been created where the porphyrin moieties are either incorporated as struts within the framework to form porphyrinic MOFs or encapsulated inside the cavities to construct porphyrin@MOFs which can combine the peerless properties of porphyrins and porous MOFs simultaneously. In this context, the main aim of this review was to highlight their structure, characteristics, and some of their prominent present-day applications.
Keywords: (photo-)catalysis; biomimetic; electrochemical utilization; metalloporphyrins; metal–organic frameworks; porphyrins; synthetic strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Zaamani S., Abbasi A., Masteri-Farahani M., Rayati S. One-pot, facile synthesis and fast separation of a UiO-66 composite by a metalloporphyrin using nanomagnetic materials for oxidation of olefins and allylic alcohols. New J. Chem. 2022;46:654–662. doi: 10.1039/D1NJ04828G. - DOI
-
- Zhang K., Goswami S., Noh H., Lu Z., Sheridan T., Duan J., Dong W., Hupp J.T. An Iron-Porphyrin Grafted Metal–Organic Framework as a Heterogeneous Catalyst for the Photochemical Reduction of CO2. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2022;10:100111. doi: 10.1016/j.jpap.2022.100111. - DOI
-
- Gutov O.V., Bury W., Gomez-Gualdron D.A., Krungleviciute V., Fairen-Jimenez D., Mondloch J.E., Sarjeant A.A., Al-Juaid S.S., Snurr R.Q., Hupp J.T., et al. Water-Stable Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Framework Material with High-Surface Area and Gas-Storage Capacities. Chem. Eur. J. 2014;20:12389–12393. doi: 10.1002/chem.201402895. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

