New Quinoxaline-Based Derivatives as PARP-1 Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Antiproliferative, and Computational Studies
- PMID: 35956876
- PMCID: PMC9370283
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154924
New Quinoxaline-Based Derivatives as PARP-1 Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, Antiproliferative, and Computational Studies
Abstract
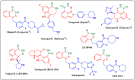
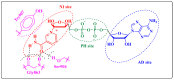
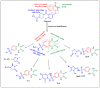
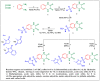
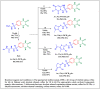
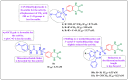
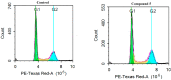
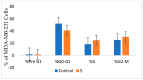
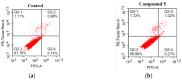
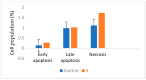
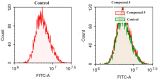
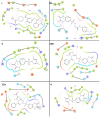
Herein, 2,3-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline was used as a bio-isosteric scaffold to the phthalazinone motif of the standard drug Olaparib to design and synthesize new derivatives of potential PARP-1 inhibitory activity using the 6-sulfonohydrazide analog 3 as the key intermediate. Although the new compounds represented the PARP-1 suppression impact of IC50 values in the nanomolar range, compounds 8a, 5 were the most promising suppressors, producing IC50 values of 2.31 and 3.05 nM compared to Olaparib with IC50 of 4.40 nM. Compounds 4, 10b, and 11b showed a mild decrease in the potency of the IC50 range of 6.35-8.73 nM. Furthermore, compounds 4, 5, 8a, 10b, and 11b were evaluated as in vitro antiproliferative agents against the mutant BRCA1 (MDA-MB-436, breast cancer) compared to Olaparib as a positive control. Compound 5 exhibited the most significant potency of IC50; 2.57 µM, whereas the IC50 value of Olaparib was 8.90 µM. In addition, the examined derivatives displayed a promising safety profile against the normal WI-38 cell line. Cell cycle, apoptosis, and autophagy analyses were carried out in the MDA-MB-436 cell line for compound 5, which exhibited cell growth arrest at the G2/M phase, in addition to induction of programmed apoptosis and an increase in the autophagic process. Molecular docking of the compounds 4, 5, 8a, 10b, and 11b into the active site of PARP-1 was carried out to determine their modes of interaction. In addition, an in silico ADMET study was performed. The results evidenced that compound 5 could serve as a new framework for discovering new potent anticancer agents targeting the PARP-1 enzyme.
Keywords: ADME parameters; MDA-MB-436; PARP-1 inhibitor; WI-38; antiproliferative; apoptosis; autophagy; cell cycle; molecular docking; quinoxaline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design, synthesis and antitumor activities of phthalazinone derivatives as PARP-1 inhibitors and PARP-1/HDAC-1 inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2024 Oct;151:107556. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107556. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Bioorg Chem. 2024. PMID: 39068717
-
Carbamoylation at C-8 position of natural 3-arylcoumarin scaffold for the discovery of novel PARP-1 inhibitors with potent anticancer activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2024 Nov 5;277:116726. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116726. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Eur J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39116535
-
Targeting DNA repair mechanisms: Spirobenzoxazinone and salicylamide derivatives as novel candidates for PARP-1 inhibition in cancer therapy.Bioorg Med Chem. 2025 Jul 1;124:118173. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2025.118173. Epub 2025 Mar 23. Bioorg Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40252565
-
2-Anilinopyrimidine derivatives: Design, synthesis, in vitro anti-proliferative activity, EGFR and ARO inhibitory activity, cell cycle analysis and molecular docking study.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jun;99:103798. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103798. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32247112 Review.
-
Targeting the interplay between MMP-2, CA II and VEGFR-2 via new sulfonamide-tethered isomeric triazole hybrids; Microwave-assisted synthesis, computational studies and evaluation.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Jul;124:105816. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105816. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35489270 Review.
Cited by
-
A Theoretical Study of the Interaction of PARP-1 with Natural and Synthetic Inhibitors: Advances in the Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 27;46(9):9415-9429. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090558. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329910 Free PMC article.
-
Recent updates in click and computational chemistry for drug discovery and development.Front Chem. 2023 Feb 7;11:1114970. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1114970. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 36825226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New pyrazolopyridine and pyrazolothiazole-based compounds as anti-proliferative agents targeting c-Met kinase inhibition: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and computational studies.RSC Adv. 2023 Apr 25;13(19):12889-12905. doi: 10.1039/d3ra01931d. eCollection 2023 Apr 24. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37114032 Free PMC article.
-
New thiazolidin-4-ones as anti-cervical cancer agents targeting EGFR: design, synthesis, and computational studies.Future Med Chem. 2025 Jan;17(1):75-91. doi: 10.1080/17568919.2024.2437976. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Future Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39651653
References
-
- Guo C., Wang L., Li X., Wang S., Yu X., Xu K., Zhao Y., Luo J., Li X., Jiang B., et al. Discovery of novel bromophenol-thiosemicarbazone hybrids as potent selective inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) for use in cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2019;62:3051–3067. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01946. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Velagapudi U.K., Langelier M.F., Delgado-Martin C., Diolaiti M.E., Bakker S., Ashworth A., Patel B.A., Shao X., Pascal J.M., Talele T.T. Design and synthesis of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors: Impact of adenosine pocket-binding motif appendage to the 3-oxo-2, 3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-carboxamide on potency and selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2019;62:5330–5357. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b01709. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

