Insights into the Explicit Protective Activity of Herbals in Management of Neurodegenerative and Cerebrovascular Disorders
- PMID: 35956919
- PMCID: PMC9370592
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27154970
Insights into the Explicit Protective Activity of Herbals in Management of Neurodegenerative and Cerebrovascular Disorders
Abstract
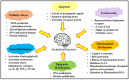
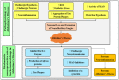
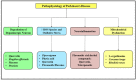
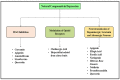
The longstanding progressive neurodegenerative conditions of the central nervous system arise mainly due to deterioration, degradation and eventual neuronal cell loss. As an individual ages, the irreversible neurodegenerative disorders associated with aging also begin to develop, and these have become exceedingly prominent and pose a significant burden mentally, socially and economically on both the individual and their family. These disorders express several symptoms, such as tremors, dystonia, loss of cognitive functions, impairment of motor activity leading to immobility, loss of memory and many more which worsen with time. The treatment employed in management of these debilitating neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease (which mainly involves the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the nigrostriatal region), Alzheimer's disease (which arises due to accumulation of Tau proteins causing diffusive atrophy in the brain), Huntington's disease (which involves damage of striatal and spinal neurons, etc.), have several adverse effects, leading to exploration of several lead targets and molecules existing in herbal drugs. The current review highlights the mechanistic role of natural products in the treatment of several neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, ischemic stroke and depression.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; bioactive compounds; natural products; neurodegenerative disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
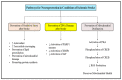
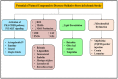
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

