Transcriptome Analysis of the Anti-Proliferative Effects of Ginsenoside Rh3 on HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35956952
- PMCID: PMC9370307
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27155002
Transcriptome Analysis of the Anti-Proliferative Effects of Ginsenoside Rh3 on HCT116 Colorectal Cancer Cells
Abstract
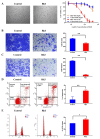
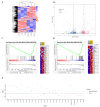
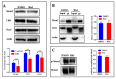
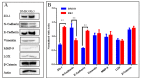
The mechanism of ginsenoside Rh3 activity against cancer remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the underlying mechanism. The effects of Rh3 on the cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and cycle and apoptosis were analyzed using CCK-8 assay, transwell migration assay and flow cytometry, respectively. The RNA transcriptome was sequenced and data were analyzed by R software. Protein expression and protein-protein interactions were determined by Western blotting and co-immunoprecipitation, respectively. The results showed Rh3 inhibited HCT116 cell proliferation, invasion, and migration, arrested cells at G1 phase; and increased apoptosis. Rh3 downregulated 314 genes and upregulated 371 genes. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) using The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes Genomics ranked DNA replication first, while GSEA using Gene Ontology ranked the initiation of DNA replication first. Compared with tumor data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), most of genes related to DNA replication were oppositely regulated by Rh3. Furthermore, Rh3 down-regulated key protein expression related to DNA replication (Orc6, Cdt1, and Mcm2), but did not affect the loading of Mcm complexes onto ORC complexes nor the phosphorylation at ser139 of Mcm2. Therefore, Rh3 may inhibit colorectal cancer HCT116 cells by downregulation of genes related to DNA replication.
Keywords: DNA replication; colorectal cancer; ginsenoside (Rh3); proliferation; transcriptome analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

