Analysis of VOCs in Urine Samples Directed towards of Bladder Cancer Detection
- PMID: 35956972
- PMCID: PMC9370153
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27155023
Analysis of VOCs in Urine Samples Directed towards of Bladder Cancer Detection
Abstract
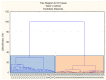
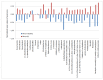
Bladder cancer is one of most common types of cancer diagnosed in the genitourinary tract. Typical tests are costly and characterized by low sensitivity, which contributes to a growing interest in volatile biomarkers. Head space solid phase microextraction (SPME) was applied for the extraction of volatile organic compounds from urine samples, and gas chromatography time of flight mass spectrometry (GC×GC TOF MS) was used for the separation and detection of urinary volatiles. A cohort of 40 adult patients with bladder cancer and 57 healthy persons was recruited. Different VOC profiles were obtained for urine samples taken from each group. Twelvecompounds were found only in the samples from theBC group.The proposed candidate biomarkers are butyrolactone; 2-methoxyphenol; 3-methoxy-5-methylphenol; 1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexa-1,3-dien-1-yl)-2-buten-1-one; nootkatone and 1-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexenyl)-2-buten-1-one.Since most of the studies published in the field are proving the potential of VOCs detected in urine samples for the screening and discrimination of patients with bladder cancer from healthy, but rarely presenting the identity of proposed biomarkers, our study represents a novel approach.
Keywords: GC×GC TOF MS; bladder cancer; urine analyses; volatile organic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Cumberbatch M.G.K., Jubber I., Black P.C., Esperto F., Figueroa J.D., Kamat A.M., Kiemeney L., Lotan Y., Pang K., Silverman D.T., et al. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Contemporary Update of Risk Factors in 2018. Eur. Urol. 2018;74:784–795. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.09.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

