Nanotechnological Interventions in Agriculture
- PMID: 35957097
- PMCID: PMC9370753
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12152667
Nanotechnological Interventions in Agriculture
Abstract
Agriculture is an important sector that plays an important role in providing food to both humans and animals. In addition, this sector plays an important role in the world economy. Changes in climatic conditions and biotic and abiotic stresses cause significant damage to agricultural production around the world. Therefore, the development of sustainable agricultural techniques is becoming increasingly important keeping in view the growing population and its demands. Nanotechnology provides important tools to different industrial sectors, and nowadays, the use of nanotechnology is focused on achieving a sustainable agricultural system. Great attention has been given to the development and optimization of nanomaterials and their application in the agriculture sector to improve plant growth and development, plant health and protection and overall performance in terms of morphological and physiological activities. The present communication provides up-to-date information on nanotechnological interventions in the agriculture sector. The present review deals with nanoparticles, their types and the role of nanotechnology in plant growth, development, pathogen detection and crop protection, its role in the delivery of genetic material, plant growth regulators and agrochemicals and its role in genetic engineering. Moreover, the role of nanotechnology in stress management is also discussed. Our aim in this review is to aid researchers to learn quickly how to use plant nanotechnology for improving agricultural production.
Keywords: abiotic stress; nanomaterials; nanoparticles; nanotechnology; sustainable agriculture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
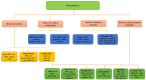
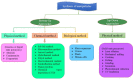
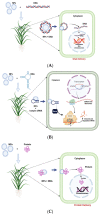






References
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division . World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423) Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division; New York, NY, USA: 2019.
-
- Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) The State of Food and Agriculture: Moving Forward on Food and Waste Reduction. Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO); Rome, Italy: 2019. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
-
- Faraji J., Sepehri A. Exogenous nitric oxide improves the protective effects of TiO2 nanoparticles on growth, antioxidant system, and photosynthetic performance of wheat seedlings under drought stress. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020;20:703–714. doi: 10.1007/s42729-019-00158-0. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

