An Energy-Efficient Clustering Method for Target Tracking Based on Tracking Anchors in Wireless Sensor Networks
- PMID: 35957232
- PMCID: PMC9371144
- DOI: 10.3390/s22155675
An Energy-Efficient Clustering Method for Target Tracking Based on Tracking Anchors in Wireless Sensor Networks
Abstract
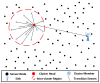
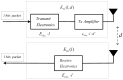
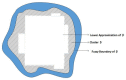
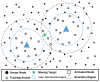
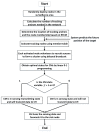
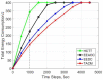
As a key technology in wireless sensor networks (WSNs), target tracking plays an essential role in many applications. To improve energy efficiency, clustering is widely used in tracking to organize the network to achieve data fusion and reduce communication costs. Many existing studies make dynamic adjustments based on static clusters to track moving targets. However, the additional overhead caused by frequent cluster reconstruction and redundant data transmission is rarely considered. To address this issue, we propose a tracking-anchor-based clustering method (TACM) in this paper, in which tracking anchors are introduced to provide activation indications for sensors according to the target position. We use the rough fuzzy C-means (RFCM) algorithm to locate the anchors and use the membership table to activate sensors to form a cluster. Since there are no sending, receiving, and fusing data tasks for anchors, they are lightly burdened and can significantly reduce the frequency of being rotated. Moreover, the state of cluster members (CMs) is scheduled using the linear 0-1 programming to reduce redundant transmissions. The simulation results demonstrate that, compared with some existing clustering methods, the proposed TACM effectively reduces the energy consumption when tracking a moving target, thus prolonging the network lifetime.
Keywords: clustering method; energy efficiency; target tracking; wireless sensor networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Xie H.M., Yan Z., Yao Z., Atiquzzaman M. Data Collection for Security Measurement in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things. 2019;6:2205–2224. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2883403. - DOI
-
- Yang H., Feng Z.X., Teng X.L., Guan L., Hu H., Wu M.B. Three-dimensional printing of high-mass loading electrodes for energy storage applications. InfoMat. 2020;3:631–647. doi: 10.1002/inf2.12181. - DOI
-
- Jamshed M.A., Ali K., Abbasi Q.H., Imran M.A., Ur-Rehman M. Challenges, Applications, and Future of Wireless Sensors in Internet of Things: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022;22:5482–5494. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3148128. - DOI
-
- Rashid B., Rehmani M.H. Applications of wireless sensor networks for urban areas: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016;60:192–219. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2015.09.008. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

