Convolutional Neural Network Applied to SARS-CoV-2 Sequence Classification
- PMID: 35957287
- PMCID: PMC9371030
- DOI: 10.3390/s22155730
Convolutional Neural Network Applied to SARS-CoV-2 Sequence Classification
Abstract
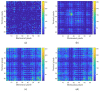
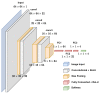
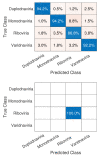
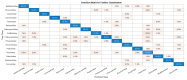
COVID-19, the illness caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus belonging to the Coronaviridade family, a single-strand positive-sense RNA genome, has been spreading around the world and has been declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization. On 17 January 2022, there were more than 329 million cases, with more than 5.5 million deaths. Although COVID-19 has a low mortality rate, its high capacities for contamination, spread, and mutation worry the authorities, especially after the emergence of the Omicron variant, which has a high transmission capacity and can more easily contaminate even vaccinated people. Such outbreaks require elucidation of the taxonomic classification and origin of the virus (SARS-CoV-2) from the genomic sequence for strategic planning, containment, and treatment of the disease. Thus, this work proposes a high-accuracy technique to classify viruses and other organisms from a genome sequence using a deep learning convolutional neural network (CNN). Unlike the other literature, the proposed approach does not limit the length of the genome sequence. The results show that the novel proposal accurately distinguishes SARS-CoV-2 from the sequences of other viruses. The results were obtained from 1557 instances of SARS-CoV-2 from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and 14,684 different viruses from the Virus-Host DB. As a CNN has several changeable parameters, the tests were performed with forty-eight different architectures; the best of these had an accuracy of 91.94 ± 2.62% in classifying viruses into their realms correctly, in addition to 100% accuracy in classifying SARS-CoV-2 into its respective realm, Riboviria. For the subsequent classifications (family, genera, and subgenus), this accuracy increased, which shows that the proposed architecture may be viable in the classification of the virus that causes COVID-19.
Keywords: CNN; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; deep learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Deepvirusclassifier: a deep learning tool for classifying SARS-CoV-2 based on viral subtypes within the coronaviridae family.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Jul 5;25(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05754-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38969970 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Dynamics of Omicron (BA.1, BA.2, and BA.5) Waves and Emergence of the Deltacton Variant: Genomic Epidemiology of the SARS-CoV-2 Epidemic in Cyprus (Oct 2021-Oct 2022).Viruses. 2023 Sep 15;15(9):1933. doi: 10.3390/v15091933. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37766339 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 virus classification based on stacked sparse autoencoder.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023;21:284-298. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.12.007. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36530948 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, molecular, and epidemiological characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), a comprehensive literature review.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Sep;98(1):115094. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2020.115094. Epub 2020 May 30. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32623267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Topological Analysis for Sequence Variability: Case Study on more than 2K SARS-CoV-2 sequences of COVID-19 infected 54 countries in comparison with SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV.Infect Genet Evol. 2021 Mar;88:104708. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104708. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Infect Genet Evol. 2021. PMID: 33421654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
On leveraging self-supervised learning for accurate HCV genotyping.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 5;14(1):15463. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64209-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38965254 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Algorithms Associate Case Numbers with SARS-CoV-2 Variants Rather Than with Impactful Mutations.Viruses. 2023 May 24;15(6):1226. doi: 10.3390/v15061226. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37376526 Free PMC article.
-
Multifractal analysis and support vector machine for the classification of coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 variants.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 29;15(1):15041. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98366-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40301538 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Neural Network Performance in Predicting Disease Status and Tissue Source of JC Polyomavirus from Patient Isolates Based on the Hypervariable Region of the Viral Genome.Viruses. 2024 Dec 25;17(1):12. doi: 10.3390/v17010012. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39861801 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

