Long-term safety of MRI-guided administration of AAV2-GDNF and gadoteridol in the putamen of individuals with Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 35957524
- PMCID: PMC9734022
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.08.003
Long-term safety of MRI-guided administration of AAV2-GDNF and gadoteridol in the putamen of individuals with Parkinson's disease
Erratum in
-
Long-term safety of MRI-guided administration of AAV2-GDNF and gadoteridol in the putamen of individuals with Parkinson's disease.Mol Ther. 2023 Jul 5;31(7):2296. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.04.009. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37098347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
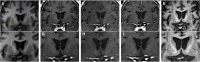
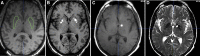
Direct putaminal infusion of adeno-associated virus vector (serotype 2) (AAV2) containing the human glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) transgene was studied in a phase I clinical trial of participants with advanced Parkinson's disease (PD). Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV2-GDNF with a surrogate imaging tracer (gadoteridol) was used to track infusate distribution during real-time intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (iMRI). Pre-, intra-, and serial postoperative (up to 5 years after infusion) MRI were analyzed in 13 participants with PD treated with bilateral putaminal co-infusions (52 infusions in total) of AAV2-GDNF and gadoteridol (infusion volume, 450 mL per putamen). Real-time iMRI confirmed infusion cannula placement, anatomic quantification of volumetric perfusion within the putamen, and direct visualization of off-target leakage or cannula reflux (which permitted corresponding infusion rate/cannula adjustments). Serial post-treatment MRI assessment (n = 13) demonstrated no evidence of cerebral parenchyma toxicity in the corresponding regions of AAV2-GDNF and gadoteridol co-infusion or surrounding regions over long-term follow-up. Direct confirmation of key intraoperative safety and efficacy parameters underscores the safety and tissue targeting value of real-time imaging with co-infused gadoteridol and putative therapeutic agents (i.e., AAV2-GDNF). This delivery-imaging platform enhances safety, permits delivery personalization, improves therapeutic distribution, and facilitates assessment of efficacy and dosing effect.
Keywords: AAV; GDNF; MRI-guided; Parkinson's disease; convection-enhanced delivery; gadoteridol; gene therapy; putamen; safety.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.S.F. is an employee of Asklepios BioPharmaceutical, Inc. (AskBio). C.L. reports honoraria for editorial work from Elsevier, Inc. The work submitted here was conducted in the course of employment for the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, an agency of the US Government. K.S.B. is a consultant to AskBio, Aviado Bio, and Scribe Tx and a patent holder on relevant technologies utilized in this study. K.S.B. was a co-founder of Voyager Therapeutics, has not been associated with the company for over 3 years, and reports no current financial interests in that company.
Figures



References
-
- Krauze M.T., McKnight T.R., Yamashita Y., Bringas J., Noble C.O., Saito R., Geletneky K., Forsayeth J., Berger M.S., Jackson P., et al. Real-time visualization and characterization of liposomal delivery into the monkey brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Brain. Res. Brain. Res. Protoc. 2005;16:20–26. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresprot.2005.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

