Identification of novel biomarkers in septic cardiomyopathy via integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
- PMID: 35957694
- PMCID: PMC9358039
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.929293
Identification of novel biomarkers in septic cardiomyopathy via integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
Abstract
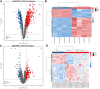
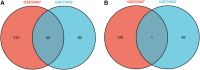
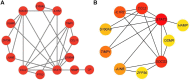
Purpose: Septic cardiomyopathy (SCM) is an important world public health problem with high morbidity and mortality. It is necessary to identify SCM biomarkers at the genetic level to identify new therapeutic targets and strategies. Method: DEGs in SCM were identified by comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of microarray datasets (GSE53007 and GSE79962) downloaded from the GEO database. Subsequently, bioinformatics analysis was used to conduct an in-depth exploration of DEGs, including GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis, PPI network construction, and key gene identification. The top ten Hub genes were identified, and then the SCM model was constructed by treating HL-1 cells and AC16 cells with LPS, and these top ten Hub genes were examined using qPCR. Result: STAT3, SOCS3, CCL2, IL1R2, JUNB, S100A9, OSMR, ZFP36, and HAMP were significantly elevated in the established SCM cells model. Conclusion: After bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification, it was demonstrated that STAT3, SOCS3, CCL2, IL1R2, JUNB, S100A9, OSMR, ZFP36, and HAMP might play important roles in SCM.
Keywords: biomarkers; differentially expressed genes; integrated bioinformatics analysis; sepsis; septic cardiomyopathy.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Hu, Qiu, Zou and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unveiling Key Biomarkers and Mechanisms in Septic Cardiomyopathy: A Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Dec 23;17:11451-11467. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S486763. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39735900 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of mitochondrial metabolic dysregulation and immune infiltration in septic cardiomyopathy by integrated bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Jan 30;29(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00536-2. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38291374 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of STAT3 and MYC as critical ferroptosis-related biomarkers in septic cardiomyopathy: a bioinformatics and experimental study.J Mol Med (Berl). 2025 Jan;103(1):87-100. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02502-z. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Mol Med (Berl). 2025. PMID: 39557695
-
Exploring potential therapeutic agents for lipopolysaccharide-induced septic cardiomyopathy based on transcriptomics using bioinformatics.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 23;13(1):20589. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47699-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37996554 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Ferroptosis-Related Biomarkers in Septic Cardiomyopathy via Bioinformatics Analysis.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 13;13:827559. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.827559. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35495160 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From cardiac injury to omics signatures: a narrative review on biomarkers in septic cardiomyopathy.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Aug 21;25(1):298. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01842-5. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40839200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics analysis reveals the interplay between pulmonary microbiome and host in immunocompromised patients with sepsis-induced acute lung injury.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 18;12(12):e0142424. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01424-24. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39422492 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Key Biomarkers and Mechanisms in Septic Cardiomyopathy: A Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Dec 23;17:11451-11467. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S486763. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39735900 Free PMC article.
-
BMP10 Knockdown Modulates Endothelial Cell Immunoreactivity by Inhibiting the HIF-1α Pathway in the Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Nov;28(22):e70232. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70232. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39611400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen L., Long X., Xu Q., Tan J., Wang G., Cao Y., et al. (2020a). Elevated serum levels of S100A8/A9 and HMGB1 at hospital admission are correlated with inferior clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients.Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't]. J. Artic. Mol. Immunol. 17 (9), 992–994. 10.1038/s41423-020-0492-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

