Effect of quercetin on muscle growth and antioxidant status of the dark sleeper Odontobutis potamophila
- PMID: 35957695
- PMCID: PMC9358148
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.938526
Effect of quercetin on muscle growth and antioxidant status of the dark sleeper Odontobutis potamophila
Abstract
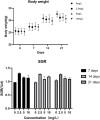
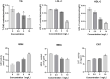
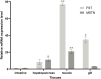
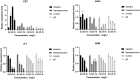
Quercetin is a flavanol beneficial in reducing fat, promoting muscle growth, and Anti-oxidation. To study its effects in freshwater fish, the full-length cDNA of the follistatin (FST) and myostatin (MSTN) genes of the dark sleeper Odontobutis potamophila were cloned for the first time. Juvenile individual O. potamophila was exposed to quercetin at one of four concentrations (0, 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/L) for 21 days. The expression level of MSTN which inhibits muscle growth in the quercetin solution was lower than in the unexposed control group. The genes that promote muscle growth are in TGF-β superfamily like FST, TGF-β1 (transforming growth factor-beta 1), and Myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) like Myf5 (myogenic factor 5), MyoD (myogenic differentiation), MyoG (myogenin), were higher than in the control group. Apolipoprotein and growth hormone receptor transcription levels in the quercetin-treated fish were significantly lower than in the control group. The concentrations of triglyceride, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the muscle tissue decreased, and the lipid-lowering function of quercetin was also demonstrated at the biochemical level. In this study, we analyzed the mRNA levels of AKT, Keap1 (kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1), Nrf2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) oxidation-related genes in the Nrf2/ARE antioxidant pathway, and Malondialdehyde (MDA), catalase (CAT) activity and glutathione (GSH) content in the hepatopancreas of O. potamophila after quercetin treatment, the mRNA expression of AKT, Nrf2 and CAT activity and GSH content are higher than in the control group. Quercetin enhances antioxidant properties and positively affects muscle growth. The results showed that quercetin has no significant effects on the growth performance of O. potamophila, but is effective in increasing muscle growth rate and lowering muscle fat content.
Keywords: Odontobutis potamophila; antioxidant; flesh quality; muscle growth-related gene; quercetin.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Liu, Gu, Yin, Xia, Han, Zhang and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
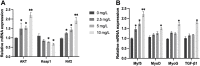
Similar articles
-
Effects of Quercetin on the Intestinal Microflora of Freshwater Dark Sleeper Odontobutis potamophila.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;11(10):2015. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290739 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary conservation and divergence of Vasa, Dazl and Nanos1 during embryogenesis and gametogenesis in dark sleeper (Odontobutis potamophila).Gene. 2018 Sep 25;672:21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.016. Epub 2018 Jun 6. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29885464
-
Proteomics-Based Investigation of Different Live Prey Administered to Freshwater Dark Sleeper (Odontobutis potamophila): Examining the Effects on Glycolipids and Energy Metabolism.Metabolites. 2024 Jan 24;14(2):85. doi: 10.3390/metabo14020085. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38392977 Free PMC article.
-
A Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of the Dark Sleeper Odontobutis potamophila.Genome Biol Evol. 2021 Feb 3;13(2):evaa271. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa271. Genome Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 33576781 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary isoleucine improved flesh quality, muscle antioxidant capacity, and muscle growth associated with AKT/TOR/S6K1 and AKT/FOXO3a signaling in hybrid bagrid catfish (Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂).J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 19;12(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00572-4. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33866964 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals a cellular immune response in freshwater dark sleeper (Odontobutis potamophila) after infection with Aeromonas veronii.Front Physiol. 2023 May 18;14:1201914. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1201914. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37275236 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Quercetin on the Intestinal Microflora of Freshwater Dark Sleeper Odontobutis potamophila.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;11(10):2015. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290739 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin as an Antioxidant for Bone-Muscle-Tendon Regeneration and Aging.Aging Dis. 2024 Jun 24;16(3):1414-1437. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0282. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 39012676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aebi H. (1984). “[13] catalase in vitro ,” in Methods in enzymology (Elsevier; ), 121–126. - PubMed
-
- Andrés S., Tejido M. L., Bodas R., Morán L., Prieto N., Blanco C., et al. (2013). Quercetin dietary supplementation of fattening lambs at 0.2% rate reduces discolouration and microbial growth in meat during refrigerated storage. Meat Sci. 93 (2), 207–212. 10.1016/j.meatsci.2012.08.023 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

