Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α in metabolic reprogramming in renal fibrosis
- PMID: 35957825
- PMCID: PMC9357883
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.927329
Molecular mechanisms underlying the role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α in metabolic reprogramming in renal fibrosis
Abstract
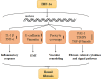
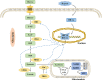
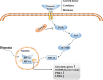
Renal fibrosis is the result of renal tissue damage and repair response disorders. If fibrosis is not effectively blocked, it causes loss of renal function, leading to chronic renal failure. Metabolic reprogramming, which promotes cell proliferation by regulating cellular energy metabolism, is considered a unique tumor cell marker. The transition from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis is a major feature of renal fibrosis. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 α (HIF-1α), a vital transcription factor, senses oxygen status, induces adaptive changes in cell metabolism, and plays an important role in renal fibrosis and glucose metabolism. This review focuses on the regulation of proteins related to aerobic glycolysis by HIF-1α and attempts to elucidate the possible regulatory mechanism underlying the effects of HIF-1α on glucose metabolism during renal fibrosis, aiming to provide new ideas for targeted metabolic pathway intervention in renal fibrosis.
Keywords: aerobic glycolysis; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; metabolic reprogramming; oxidative phosphorylation; renal fibrosis.
Copyright © 2022 Wei, Hou, Long, Jiang and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIF-1α: A potential therapeutic opportunity in renal fibrosis.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Jan 5;387:110808. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110808. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 37980973 Review.
-
HIF-1α switches the functionality of TGF-β signaling via changing the partners of smads to drive glucose metabolic reprogramming in non-small cell lung cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 20;40(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02188-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34930376 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α/Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 1 Axis by Dichloroacetate Suppresses Bleomycin-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 Feb;58(2):216-231. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0186OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 28915065 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-1-Dependent Reprogramming of Glucose Metabolic Pathway of Cancer Cells and Its Therapeutic Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 9;20(2):238. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020238. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30634433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor regulates glucose metabolism through glucose transporter 1 induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in adipocytes.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;43(11):1602-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21810481
Cited by
-
Glycolytic enzymes in non-glycolytic web: functional analysis of the key players.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):351-378. doi: 10.1007/s12013-023-01213-5. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38196050 Review.
-
Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor on immobilization-induced muscle fibrosis related to muscle contracture.J Phys Ther Sci. 2025 Jul;37(7):348-354. doi: 10.1589/jpts.37.348. Epub 2025 Jul 1. J Phys Ther Sci. 2025. PMID: 40599839 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha (HIF-1α): An Essential Regulator in Cellular Metabolic Control.Cureus. 2024 Jul 4;16(7):e63852. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63852. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39099978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaced roles of desmoplastic reaction and fibrosis in pancreatic cancer progression: Current understanding and future directions.Cancer Sci. 2023 Sep;114(9):3487-3495. doi: 10.1111/cas.15890. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 37480223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived membrane particles suppress kidney fibrosis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jul 26;16(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04522-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40713899 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

