Partial Nephrectomy Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Endophytic Renal Tumors: Comparison of Operative, Functional, and Oncological Outcomes by Propensity Score Matching Analysis
- PMID: 35957884
- PMCID: PMC9360524
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.916018
Partial Nephrectomy Versus Radical Nephrectomy for Endophytic Renal Tumors: Comparison of Operative, Functional, and Oncological Outcomes by Propensity Score Matching Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: The study aimed to compare operative, functional, and oncological outcomes between partial nephrectomy (PN) and radical nephrectomy (RN) for entophytic renal tumors (ERTs) by propensity score matching (PSM) analysis.
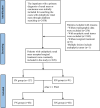
Methods: A total of 228 patients with ERTs who underwent PN or RN between August 2014 and December 2021 were assessed. A PSM in a 1:1 ratio was conducted to balance the differences between groups. Perioperative characteristics, renal functional, and oncological outcomes were compared between groups. Univariate and multivariate logistic and Cox proportional hazard regression analyses were used to determine the predictors of functional and survival outcomes.
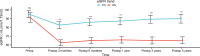
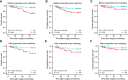
Results: After PSM, 136 cases were matched to the PN group (n = 68) and the RN group (n = 68). Patients who underwent RN had shorter OT, less EBL, and lower high-grade complications (all p <0.05) relative to those who underwent PN. However, better perseveration of renal function was observed in the PN group, which was reflected in 48-h postoperative AKI (44.1% vs. 70.6%, p = 0.002), 1-year postoperative 90% eGFR preservation (45.6% vs. 22.1%, p = 0.004), and new-onset CKD Stage ≥III at last follow-up (2.9% vs. 29.4%, p <0.001). RN was the independent factor of short-term (OR, 2.812; 95% CI, 1.369-5.778; p = 0.005) and long-term renal function decline (OR, 10.242; 95% CI, 2.175-48.240; p = 0.003). Furthermore, PN resulted in a better OS and similar PFS and CSS as compared to RN (p = 0.042, 0.15, and 0.21, respectively). RN (OR, 7.361; 95% CI, 1.143-47.423; p = 0.036) and pT3 stage (OR, 4.241; 95% CI, 1.079-16.664; p = 0.039) were independent predictors of overall mortality.
Conclusion: Among patients with ERTs, although the PN group showed a higher incidence of high-grade complications than RN, when technically feasible and with experienced surgeons, PN is recommended for better preservation of renal function, longer OS, and similar oncological outcomes.
Keywords: endophytic renal tumor; function outcomes; oncological outcomes; operative outcomes; partial nephrectomy; propensity score matching; radical nephrectomy.
Copyright © 2022 Xiong, Jiang, Jiang, Hu, Chen, Yao, Deng, Wan, Liu, Chen and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oncological and functional efficacy of nephron-sparing surgery versus radical nephrectomy in renal cell carcinoma stages ≥cT1b: a single institution, matched analysis.Cent European J Urol. 2018;71(1):48-57. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2017.1611. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Cent European J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29732207 Free PMC article.
-
Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of Radical and Partial Nephrectomy in pT3aN0M0 Renal Cell Carcinoma.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025 Jun;23(3):102343. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2025.102343. Epub 2025 Apr 4. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40286515
-
Partial versus radical nephrectomy in very elderly patients: a propensity score analysis of surgical, functional and oncologic outcomes (RESURGE project).World J Urol. 2020 Jan;38(1):151-158. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02665-2. Epub 2019 Apr 1. World J Urol. 2020. PMID: 30937569
-
Partial nephrectomy versus radical nephrectomy for large (≥ 7 cm) renal tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Urol Oncol. 2019 Apr;37(4):263-272. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.12.015. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Urol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30704957
-
Comparison of the long-term follow-up and perioperative outcomes of partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy for 4 cm to 7 cm renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Urol. 2019 Jun 7;19(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12894-019-0480-6. BMC Urol. 2019. PMID: 31174522 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From sutureless to standard: a comprehensive analysis of conversion rates in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy.BMC Urol. 2024 Aug 28;24(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12894-024-01578-6. BMC Urol. 2024. PMID: 39198764 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic partial nephrectomy to treat large (T2) cystic renal cell carcinoma: a multi-institutional analysis (ROSULA Collaborative Group).Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Jun 21. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04604-0. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40542967
-
Surgical Strategies in Renal Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Partial vs. Radical Nephrectomy Outcomes Across Tumor Stages.Qatar Med J. 2025 Jun 9;2025(2):54. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2025.54. eCollection 2025. Qatar Med J. 2025. PMID: 40556844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Learning Curves in Robotic Urological Oncological Surgery: Has Anything Changed During the Last Five Years?Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 15;17(8):1334. doi: 10.3390/cancers17081334. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Transabdominal Lumbar Approach (TALA) for Robotic Renal Surgery-A Retrospective Single-Center Comparative Study and Step-by-Step Description of a Novel Approach.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 20;16(2):446. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020446. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minoda R, Takagi T, Yoshida K, Kondo T, Tanabe K. Comparison of Surgical Outcomes Between Enucleation and Standard Resection in Robot-Assisted Partial Nephrectomy for Completely Endophytic Renal Tumors Through a 1:1 Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. J Endourol (2021) 35:1779–84. doi: 10.1089/end.2021.0213 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

