Sema3d Restrained Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Inactivating Pi3k/Akt Signaling via Interaction With FLNA
- PMID: 35957887
- PMCID: PMC9358705
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.913498
Sema3d Restrained Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Through Inactivating Pi3k/Akt Signaling via Interaction With FLNA
Abstract
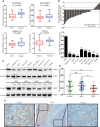
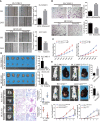
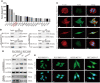
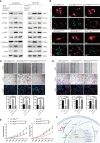
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal malignant tumors worldwide due to the high incidence rate of metastasis and recurrence. Semaphorin 3d (Sema3d) has been shown to play a critical role in vascular development during early embryogenesis and several forms of cancer progression via regulating cell migration. However, the function of Sema3d in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains elusive. This study aimed to explore the function and mechanisms of Sema3d in HCC. In our study, Sema3d expression was significantly downregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines. Downregulated Sema3d was closely correlated with aggressive clinicopathological features and poor clinical outcomes in HCC patients. Moreover, overexpression of Sema3d in HCCLM3 cells was significantly inhibited and knockdown of Sema3d in PLC/PRF/5 cells promoted proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of HCC cells in vitro and tumor growth, EMT, and metastasis in vivo. Furthermore, the RNA sequencing and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) indicated that these phenotypic and functional changes in Sema3d-interfered HCC cells were mediated by the Pi3k/Akt signaling pathway, and co-IP-combined mass spectrometry indicated Sema3d might interact with FLNA. Finally, we proved that Sema3d exerted its tumor-restraining effect by interacting with FLNA to inactivate the Pi3k/Akt signaling pathway and remodel the cytoskeleton. Our data showed that Sema3d restrained hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation, invasion, and metastasis through inactivating Pi3k/Akt via interaction with FLNA, which may serve as a novel prognostic predictor and a potential therapeutic target for HCC patients.
Keywords: EMT; Pi3k/Akt signaling; Sema3d; cancer progression; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognosis; semaphorin 3d.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Xu, Sun, Zhong, Cao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Piezo1 promoted hepatocellular carcinoma progression and EMT through activating TGF-β signaling by recruiting Rab5c.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Apr 23;22(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02574-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 35461277 Free PMC article.
-
MST4 negatively regulates the EMT, invasion and metastasis of HCC cells by inactivating PI3K/AKT/Snail1 axis.J Cancer. 2021 May 27;12(15):4463-4477. doi: 10.7150/jca.60008. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34149910 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-1296 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SRPK1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jun 12;16(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0675-y. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28606154 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of castor zinc finger 1 predicts poor prognosis and facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via MAPK/ERK signaling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 5;37(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0720-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29506567 Free PMC article.
-
miR-300 regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting the FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;103:1632-1642. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 May 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29864952
Cited by
-
Knocking down hypoxia-induced Semaphorin 6B may attenuate the progression of cervical cancer through regulating macrophage M2 polarization.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 10;23(1):776. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06692-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40640851 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis and immunotherapy significances of a cancer-associated fibroblasts-related gene signature in bladder urothelial carcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 6;15(1):622. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01505-z. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39503984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franssen B, Alshebeeb K, Tabrizian P, Marti J, Pierobon ES, Lubezky N, et al. . Differences in Surgical Outcomes Between Hepatitis B- and Hepatitis C-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Analysis of a Single North American Center. Ann Surg (2014), 260(4). doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000917 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

