A machine learning model based on ultrasound image features to assess the risk of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients: Applications of scikit-learn and SHAP
- PMID: 35957890
- PMCID: PMC9359803
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.944569
A machine learning model based on ultrasound image features to assess the risk of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients: Applications of scikit-learn and SHAP
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to determine an optimal machine learning (ML) model for evaluating the preoperative diagnostic value of ultrasound signs of breast cancer lesions for sentinel lymph node (SLN) status.
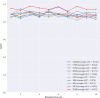
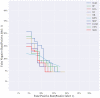
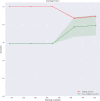
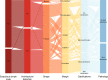
Method: This study retrospectively analyzed the ultrasound images and postoperative pathological findings of lesions in 952 breast cancer patients. Firstly, the univariate analysis of the relationship between the ultrasonographic features of breast cancer morphological features and SLN metastasis. Then, based on the ultrasound signs of breast cancer lesions, we screened ten ML models: support vector machine (SVM), extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), random forest (RF), linear discriminant analysis (LDA), logistic regression (LR), naive bayesian model (NB), k-nearest neighbors (KNN), multilayer perceptron (MLP), long short-term memory (LSTM), and convolutional neural network (CNN). The diagnostic performance of the model was evaluated using the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC), Kappa value, accuracy, F1-score, sensitivity, and specificity. Then we constructed a clinical prediction model which was based on the ML algorithm with the best diagnostic performance. Finally, we used SHapley Additive exPlanation (SHAP) to visualize and analyze the diagnostic process of the ML model.
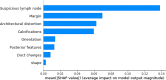
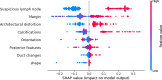
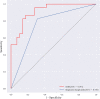
Results: Of 952 patients with breast cancer, 394 (41.4%) had SLN metastasis, and 558 (58.6%) had no metastasis. Univariate analysis found that the shape, orientation, margin, posterior features, calculations, architectural distortion, duct changes and suspicious lymph node of breast cancer lesions in ultrasound signs were associated with SLN metastasis. Among the 10 ML algorithms, XGBoost had the best comprehensive diagnostic performance for SLN metastasis, with Average-AUC of 0.952, Average-Kappa of 0.763, and Average-Accuracy of 0.891. The AUC of the XGBoost model in the validation cohort was 0.916, the accuracy was 0.846, the sensitivity was 0.870, the specificity was 0.862, and the F1-score was 0.826. The diagnostic performance of the XGBoost model was significantly higher than that of experienced radiologists in some cases (P<0.001). Using SHAP to visualize the interpretation of the ML model screen, it was found that the ultrasonic detection of suspicious lymph nodes, microcalcifications in the primary tumor, burrs on the edge of the primary tumor, and distortion of the tissue structure around the lesion contributed greatly to the diagnostic performance of the XGBoost model.
Conclusions: The XGBoost model based on the ultrasound signs of the primary breast tumor and its surrounding tissues and lymph nodes has a high diagnostic performance for predicting SLN metastasis. Visual explanation using SHAP made it an effective tool for guiding clinical courses preoperatively.
Keywords: SHAP; XGBoost; breast cancer; sentinel lymph node metastasis; ultrasound signs.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Shi, Yin, Liu, Fang, Li, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Machine Learning Model for Predicting Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Clinically Node Positive Breast Cancer Based on Peritumoral Ultrasound Radiomics and SHAP Feature Analysis.J Ultrasound Med. 2024 Sep;43(9):1611-1625. doi: 10.1002/jum.16483. Epub 2024 May 29. J Ultrasound Med. 2024. PMID: 38808580
-
Noninvasive prediction of lymph node metastasis in pancreatic cancer using an ultrasound-based clinicoradiomics machine learning model.Biomed Eng Online. 2024 Jun 18;23(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12938-024-01259-3. Biomed Eng Online. 2024. PMID: 38890695 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning for predicting neoadjuvant chemotherapy effectiveness using ultrasound radiomics features and routine clinical data of patients with breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jan 14;14:1485681. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1485681. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39927116 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretable machine learning model to predict surgical difficulty in laparoscopic resection for rectal cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 6;14:1337219. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1337219. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38380369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy of CEUS-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer: a study review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 May 29;18(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01890-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32471428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The prediction of distant metastasis risk for male breast cancer patients based on an interpretable machine learning model.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Apr 21;23(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02166-8. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37085843 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic models for breast cancer: based on logistics regression and Hybrid Bayesian Network.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Jul 13;23(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02224-1. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37443001 Free PMC article.
-
The construction of HMME-PDT efficacy prediction model for port-wine stain based on machine learning algorithms.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22563. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06589-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594548 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation Between Phyllodes Tumor and Fibroadenoma of the Breast: A Radiomics Prediction Model Based on Full-Field Digital Mammography & Digital Tomosynthesis.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241289474. doi: 10.1177/15330338241289474. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39376181 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss Recovery with Patient-Personalized Seigel's Criteria Using Machine Learning.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 19;14(12):1296. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14121296. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38928711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM, Harlow SP, Constantino JP, et al. . Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP b-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol (2010) 11(10):927–33. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70207-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

