MiR-520a-5p/PPP5C regulation pattern is identified as the key to gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 35957917
- PMCID: PMC9358958
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.903484
MiR-520a-5p/PPP5C regulation pattern is identified as the key to gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effects of the expression level of miR-520-5p/PPP5C in pancreatic cancer cells and exosomes on cell viability, angiogenesis, autophagy, which involved in the mechanism of gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer.
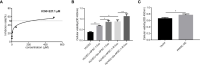
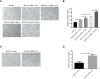
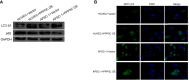
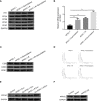
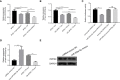
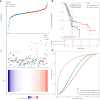
Methods: APSC-1 cell line was treated with gemcitabine, after which its exosomes were extracted for NTA assay. Subsequently, the drug resistance of APSC-1 cells was assayed using CCK8, as well as the activity of HUVEC cells treated with exosomes from each group of APSC-1 cells after drug resistance treatment as well as overexpression treatment. Five groups of HUVEC cells treated with exosomes were subjected to in vitro tubule formation assay. levels of PPP5C in each group of ASPC-1 cells and their exosomes, levels of overexpressed PPP5C, and related exosomal proteins were examined by WB. mRNA expression levels of PPP5C and levels of miR-520a were examined by qPCR The relationship between miR-520a-5p and PPP5C was investigated. After that, the autophagy of PPP5C was detected. Finally, it was analyzed by TCGA database for survival prognosis analysis.
Results: APSC-1 cells had an IC50 value of 227.1 μM for gemcitabine, elevated PPP5C expression, drug resistance, and enhanced HUVEC cell activity; exosomes CD9, CD63, and CD81 were significantly expressed in all groups; meanwhile, enhanced PPP5C expression not only promoted in vitro tubule formation but also increased autophagy levels; meanwhile, its relationship with miR-520-5p and There was a targeted inhibitory relationship between its level and miR-520-5p and PPP5C, and its elevated level also led to a decrease in the survival level of patients over 3-5 years.
Conclusion: PPP5C has a prognostic role in pancreatic cancer by promoting the value-added and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells, and a targeted inhibitory relationship between miR-520-5p and PPP5C was found.
Keywords: PPP5C; Pancreatic cancer; autophagy; gemcitabine; miR-520-5p.
Copyright © 2022 Fu, Shao, Yang, Chen, Ye, Chen and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosome-transferred hsa_circ_0014235 promotes DDP chemoresistance and deteriorates the development of non-small cell lung cancer by mediating the miR-520a-5p/CDK4 pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Nov 17;20(1):552. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01642-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 33292236 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exosomal microRNA-125b-5p in conferring the metastatic phenotype among pancreatic cancer cells with different potential of metastasis.Life Sci. 2020 Aug 15;255:117857. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117857. Epub 2020 May 27. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32470446
-
Hypoxic pancreatic cancer derived exosomal miR-30b-5p promotes tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting GJA1 expression.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(3):1220-1237. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.67675. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35173549 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-Derived Circ-PVT1 Contributes to Cisplatin Resistance by Regulating Autophagy, Invasion, and Apoptosis Via miR-30a-5p/YAP1 Axis in Gastric Cancer Cells.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021 May;36(4):347-359. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2020.3578. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021. PMID: 32799541
-
Cisplatin-resistant MDA-MB-231 Cell-derived Exosomes Increase the Resistance of Recipient Cells in an Exosomal miR-423-5p-dependent Manner.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(10):804-814. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190819151946. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 31424364
Cited by
-
Exosomal HSPB1, interacting with FUS protein, suppresses hypoxia-induced ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer by stabilizing Nrf2 mRNA and repressing P450.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(9):e18209. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18209. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38682349 Free PMC article.
-
CMTM7 inhibits breast cancer progression by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Breast Cancer Res. 2023 Feb 24;25(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01620-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36829181 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome applications for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An update (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Jan;53(1):13. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8846. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39575479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding the pancreatic cancer microenvironment: The multifaceted regulation of microRNAs.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Jul;15(7):e70354. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70354. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40579785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: their role and therapeutic potential in overcoming drug resistance of gastrointestinal cancers.Front Oncol. 2025 May 13;15:1540643. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1540643. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40432919 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

