Acupuncture Based on Regulating Autonomic Nerves for the Prevention of Migraine Without Aura: A Prospective, Double-Dummy, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
- PMID: 35957963
- PMCID: PMC9359787
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S372311
Acupuncture Based on Regulating Autonomic Nerves for the Prevention of Migraine Without Aura: A Prospective, Double-Dummy, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Migraine without aura (MWoA) is a nervous system disease, which is closely related to autonomic nerves dysfunction. As a popular non-pharmacological alternative treatment for preventing migraine, it remains unclear whether the acupuncture can prevent MWoA. Thus, this trial aims to evaluate the preventive effect and safety of the acupuncture method of stimulating acupoints that regulate autonomic nerves in MWoA patients.
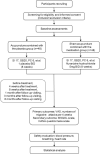
Methods: This is a single-center, prospective, double-dummy, randomized controlled clinical trial. A total of ninety-six patients with MWoA are randomly allocated to acupuncture combined with the placebo group and sham acupuncture combined with the medication group in a 1:1 ratio. All subjects will receive intervention for 8 weeks and follow-up assessments three times (one month, three months, and six months in follow-up visiting). The frequency of acupuncture in both groups is three times a week for eight weeks. The primary outcome will be evaluated using a visual analog scale (VAS) and the number of migraine attacks per four weeks. The secondary outcome measures will include the migraine-specific quality of life (MSQOL) scale and headache needs assessment survey (HANA) questionnaire scale.
Results: The acupoint selection of this clinical trial is based on the combination of traditional Chinese medicine theory with modern medicine, thereby evaluating the efficacy and safety of the acupuncture method of stimulating acupoints that regulate autonomic nerves in the prevention of MWoA. The results may provide evidence of the beneficial effects of acupuncture on the prevention of MWoA by regulating autonomic nerves dysfunction.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04766762.
Keywords: acupuncture; autonomic nerves; migraine without aura; protocol; randomized controlled clinical trial.
© 2022 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in relation to this work.
Similar articles
-
Manual acupuncture as prophylaxis for migraine without aura: study protocol for a multi-center, randomized, single-blinded trial.Trials. 2022 Jul 19;23(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06510-7. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35854329 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of contralateral acupuncture in women with migraine without aura: protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2022 Jun 24;12(6):e061287. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-061287. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35750456 Free PMC article.
-
Contralateral acupuncture for migraine without aura: a randomized trial protocol with multimodal MRI.Front Neurosci. 2024 Mar 15;18:1344235. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1344235. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38560045 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for migraine without aura: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Integr Med. 2018 Sep;16(5):312-321. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 28. J Integr Med. 2018. PMID: 30007828
-
Is Acupuncture Safe and Effective Treatment for Migraine? A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2022 Jan 3;14(1):e20888. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20888. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35145793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture Based on Regulating Autonomic Nerves for the Prevention of Migraine without Aura: A Prospective, Double-Dummy, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial [Letter].J Pain Res. 2022 Aug 22;15:2481-2482. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S385406. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36035979 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Letter to the Editor: Acupuncture Based on Regulating Autonomic Nerves for the Prevention of Migraine without Aura: A Prospective, Double-Dummy, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial [Response to Letter].J Pain Res. 2022 Sep 23;15:2997-2998. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S387388. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36176964 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous