The protective effect of MiR-27a on the neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by targeting FOXO1 in rats
- PMID: 35958013
- PMCID: PMC9360825
- DOI: 10.21037/tp-22-259
The protective effect of MiR-27a on the neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by targeting FOXO1 in rats
Abstract
Background: Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), a kind of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage caused by perinatal asphyxia, is the most crucial cause of neonatal death and long-term neurological dysfunction in children. We aimed to investigate the protective effects of micro (mi)R-27a on HIE in neonatal rats.
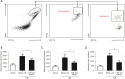
Methods: A rat model of neonatal HIE was constructed by modification of the Rice-Vannucci model. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to test the expressions of miR-27a, FOXO1 messenger RNA (mRNA), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) mRNA, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) mRNA, and western blot was applied to test the expression of FOXO1. In order to overexpress miR-27a, an intracerebroventricular injection (i.c.v) of miR-27a mimic was administered. We adopted 2,3,5-triphenytetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining and brain water content measurement to test the effects of miR-27a on the infarcted volume and edema in brain after HIE. Flow cytometry (FCM) analysis was applied to test the effects of miR-27a on the infiltrated peripheral immune cells in the rat brains after HIE.
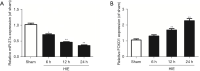
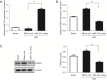
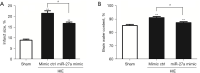
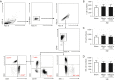
Results: We successfully established a rat model of neonatal HIE. It was revealed that the expressions of miR-27a decreased gradually after HIE, however, the expressions of FOXO1 mRNA increased. After injection of the miR-27a mimic, the expression of miR-27a in the rat HIE model brains was significantly upregulated, however, the expression of FOXO1 was robustly downregulated. Both TTC staining and brain water content showed that the infarcted volume and brain edema was markedly increased after HIE. Interestingly, the overexpression of miR-27a reduced the infarcted volume and edema induced by HIE. Additionally, RT-qPCR and FCM analysis showed that HIE lead to increases of IL-1β, TNF-α, and infiltrated immune cells. Overexpression of miR-27a could reduce the expressions of IL-1β mRNA and TNF-α mRNA, and the cell numbers of infiltrated peripheral macrophages and neutrophils in the brain.
Conclusions: MiR-27a plays protective roles by reducing infarct volume and brain edema, and inhibiting inflammatory factors and infiltrated peripheral immune cells by targeting FOXO1 in neonatal HIE rats.
Keywords: FOXO1; infarcted volume; infiltrated peripheral immune cells; inflammation; miR-27a.
2022 Translational Pediatrics. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tp.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tp-22-259/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
IRE1α inhibition attenuates neuronal pyroptosis via miR-125/NLRP1 pathway in a neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy rat model.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 May 6;17(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01796-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 32375838 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-4472 serves as a potential biomarker for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and promotes neuronal death as well as hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats by targeting MEF2D.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025 Jul 22;771:151958. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2025.151958. Epub 2025 May 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40393156
-
MiR-363-3p attenuates neonatal hypoxic-ischemia encephalopathy by targeting DUSP5.Neurosci Res. 2021 Oct;171:103-113. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2021.03.003. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Neurosci Res. 2021. PMID: 33744332
-
Research progress of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in nonhuman primate models.Ibrain. 2023 Mar 26;9(2):183-194. doi: 10.1002/ibra.12097. eCollection 2023 Summer. Ibrain. 2023. PMID: 37786551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of pentoxifylline in neonatal hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy: a systematic review of animal studies.Lab Anim Res. 2024 Nov 28;40(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s42826-024-00228-0. Lab Anim Res. 2024. PMID: 39605099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
