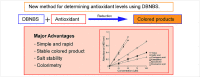
A new colorimetric method for determining antioxidant levels using 3,5-dibromo-4-nitrosobenzene sulfonate (DBNBS)
- PMID: 35958099
- PMCID: PMC9358457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2022.101797
A new colorimetric method for determining antioxidant levels using 3,5-dibromo-4-nitrosobenzene sulfonate (DBNBS)
Abstract
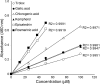
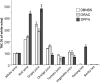
We describe here a novel assay that determines the total a+ntioxidative activities of known antioxidants and antioxidants in beverages. The method employs the substrate 3,5-dibromo-4-nitrosobenzene sulfonate (DBNBS) that yields the colored product 3,5,3',5'-tetrabromoazobenzene sulfate sodium salt (azo-TBBS). The amounts of azo-TBBS are measured using HPLC and then used to calculate total antioxidative capacity (TAC) values. We first show that the TAC values measured using the new DBNBS system were significantly higher compared with the control. The assay was validated through further analysis of 56 compounds, including previously characterized antioxidants. The data are consistent with published values. Here we describe in detail the application of the DBNBS method to the measurement of the TAC values of eight beverages, including wines and fruit juices. The DBNBS assay employs a readily applicable protocol that sensitively determines the levels of antioxidants in foodstuffs. - A new DBNBS-mediated antioxidant assay system is compared with standard DPPH and ORAC assays - DBNBS traps hydrogen radicals to generate a readily measured colored reduction product that quantifies antioxidant levels.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Antioxidative activity; Hydrogen atom transfer; Total antioxidant capacity.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

