Identification of the antibacterial action mechanism of diterpenoids through transcriptome profiling
- PMID: 35958135
- PMCID: PMC9360744
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.945023
Identification of the antibacterial action mechanism of diterpenoids through transcriptome profiling
Abstract
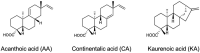
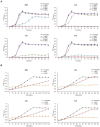
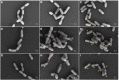
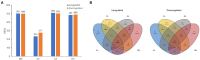
Effective antibacterial substances of Aralia continentalis have anti-biofilm and bactericidal activity to the oral pathogen Streptococcus mutans. In this study, three compounds extracted from A. continentalis were identified as acanthoic acid, continentalic acid, and kaurenoic acid by NMR and were further investigated how these diterpenoids affect the physiology of the S. mutans. When S. mutans was exposed to individual or mixed fraction of diterpenoids, severe growth defects and unique morphology were observed. The proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in the cell membrane was increased compared to that of saturated fatty acids in the presence of diterpenoids. Genome-wide gene expression profiles with RNA-seq were compared to reveal the mode of action of diterpenoids. Streptococcus mutans commonly enhanced the expression of 176 genes in the presence of the individual diterpenoids, whereas the expression of 232 genes was considerably reduced. The diterpenoid treatment modulated the expression of genes or operon(s) involved in cell membrane synthesis, cell division, and carbohydrate metabolism of S. mutans. Collectively, these findings provide novel insights into the antibacterial effect of diterpenoids to control S. mutans infection, which causes human dental caries.
Keywords: Aralia continentalis; Streptococcus mutans; antibacterial activity; diterpenoids; transcriptome analysis.
Copyright © 2022 Moon, Hwang, Lee, Jo, Kim and Cha.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of Aralia continentalis on the cariogenic properties of Streptococcus mutans.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 2;137(2):979-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.07.015. Epub 2011 Jul 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21782015
-
Ultra-performance convergence chromatography for the quantitative determination of bioactive compounds in Aralia continentalis Kitagawa as quality control markers.J Sep Sci. 2017 May;40(9):2071-2079. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201601261. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Sep Sci. 2017. PMID: 28306202
-
Antibacterial mechanism of areca nut essential oils against Streptococcus mutans by targeting the biofilm and the cell membrane.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 28;13:1140689. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1140689. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37701779 Free PMC article.
-
Dlt operon regulates physiological function and cariogenic virulence in Streptococcus mutans.Future Microbiol. 2023 Mar;18:225-233. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2022-0165. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Future Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37097048 Review.
-
Phytochemical Profile of Antibacterial Agents from Red Betel Leaf (Piper crocatum Ruiz and Pav) against Bacteria in Dental Caries.Molecules. 2022 Apr 30;27(9):2861. doi: 10.3390/molecules27092861. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35566225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Review of Traditional Medicinal Uses, Geographical Distribution, Botanical Characterization, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Aralia continentalis Kitag.Molecules. 2024 Jul 26;29(15):3529. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153529. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39124933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ent-kaurane diterpenoids from the Annonaceae family: a review of research progress and call for further research.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 29;14:1227574. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1227574. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37456746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naturally Derived Terpenoids Targeting the 3Dpol of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus: An Integrated In Silico and In Vitro Investigation.Viruses. 2024 Jul 14;16(7):1128. doi: 10.3390/v16071128. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alaki S. M., Burt B. A., Garetz S. L. (2009). The association between antibiotics usage in early childhood and early childhood caries. Pediatr. Dent. 31, 31–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

