In vitro and intracellular inhibitory activities of nosiheptide against Mycobacterium abscessus
- PMID: 35958142
- PMCID: PMC9360784
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.926361
In vitro and intracellular inhibitory activities of nosiheptide against Mycobacterium abscessus
Abstract
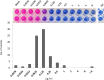
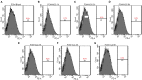
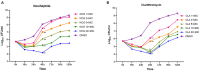
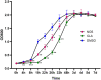
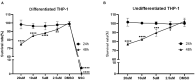
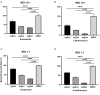
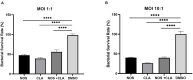
The high level of inherent drug resistance of Mycobacterium abscessus makes the infection caused by it very difficult to be treated. The objective of this study was to evaluate the potential of nosiheptide (NOS) as a new drug candidate for treating M. abscessus infections. The microplate AlamarBlue assay was performed to determine the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of NOS for 28 reference strains of rapidly growing mycobacteria (RGM) and 77 clinical isolates of M. abscessus. Time-kill kinetic and post-antibiotic effect (PAE) of NOS against M. abscessus was evaluated. Its bactericidal activity against M. abscessus in macrophages was determined by an intracellular colony numerating assay. NOS manifested good activity against the reference strains of RGM and M. abscessus clinical isolates in vitro. The MICs of NOS against M. abscessus clinical isolates ranged from 0.0078 to 1 μg/ml, and the MIC50 and MIC90 were 0.125 μg/ml and 0.25 μg/ml, respectively. The pattern of growth and kill by NOS against M. abscessus was moderate with apparent concentration-dependent characteristics, and the PAE value of NOS was found to be ~6 h. Furthermore, NOS had low cell toxicity against the THP-1 cell line after 48 h of exposure (IC50 = 106.9 μM). At 4 μg/ml, NOS exhibited high intracellular bactericidal activity against M. abscessus reference strains with an inhibitory rate of 66.52% ± 1.51%, comparable with that of clarithromycin at 2 μg/ml. NOS showed suitable inhibitory activities against M. abscessus in vitro and in macrophages and could be a potential drug candidate to treat M. abscessus infection.
Keywords: Mycobacterium abscessus; cytotoxicity; intracellular bactericidal activity; nosiheptide; susceptibility.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Yu, Zhang, Kong, Wang, Jia, Xue and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Vitro Antimicrobial Activities of Tigecycline, Eravacycline, Omadacycline, and Sarecycline against Rapidly Growing Mycobacteria.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0323822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03238-22. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36475850 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonyl Cyanide 3-Chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) Exhibits Direct Antibacterial Activity Against Mycobacterium abscessus.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Mar 23;14:1199-1208. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S303113. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 33790590 Free PMC article.
-
Nosiheptide Harbors Potent In Vitro and Intracellular Inhbitory Activities against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0144422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01444-22. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36222690 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro activity of fidaxomicin against nontuberculosis mycobacteria.J Med Microbiol. 2022 Jun;71(6). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001549. J Med Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35708979
-
Skin and soft-tissue infections due to rapidly growing mycobacteria: An overview.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2021 Jul-Sep;10(3):293-300. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_110_21. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34494569 Review.
Cited by
-
Toward a Bactericidal Oral Drug Combination for the Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease.ACS Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 11;11(4):929-939. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00948. Epub 2025 Apr 1. ACS Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40168319 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal and anti-quorum sensing activity of repurposing drug Visomitin against Staphylococcus aureus.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2415952. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2415952. Epub 2024 Oct 19. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39390774 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation rifamycins for the treatment of mycobacterial infections.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 6;122(18):e2423842122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2423842122. Epub 2025 May 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40310456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baindara P., Singh N., Ranjan M., Nallabelli N., Chaudhry V., Pathania G. L., et al. . (2016). Laterosporulin10: a novel defensin like Class IId bacteriocin from Brevibacillus sp. strain SKDU10 with inhibitory activity against microbial pathogens. Microbiology 162, 1286–1299. 10.1099/mic.0.000316 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benazet F., Cartier J. R. (1980). Effect of nosiheptide as a feed additive in chicks on the quantity, duration, prevalence of excretion, and resistance to antibacterial agents of Salmonella typhimurium; on the proportion of Escherichia coli and other coliforms resistant to antibacterial agents; and on their degree and spectrum of resistance. Poult. Sci. 59, 1405–1415. 10.3382/ps.0591405 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

