Differences in B-Cell Immunophenotypes and Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 After Administration of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccine in Individuals with and without Prior COVID-19 - A Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35958186
- PMCID: PMC9361858
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S374304
Differences in B-Cell Immunophenotypes and Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 After Administration of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Vaccine in Individuals with and without Prior COVID-19 - A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Purpose: Understanding the humoral immune response dynamics carried out by B cells in COVID-19 vaccination is little explored; therefore, we analyze the changes induced in the different cellular subpopulations of B cells after vaccination with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech).
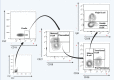
Methods: This prospective cohort study evaluated thirty-nine immunized health workers (22 with prior COVID-19 and 17 without prior COVID-19) and ten subjects not vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 (control group). B cell subpopulations (transitional, mature, naïve, memory, plasmablasts, early plasmablast, and double-negative B cells) and neutralizing antibody levels were analyzed and quantified by flow cytometry and ELISA, respectively.
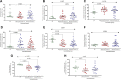
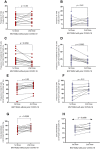
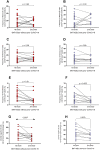
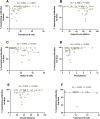
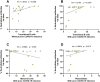
Results: The dynamics of the B cells subpopulations after vaccination showed the following pattern: the percentage of transitional B cells was higher in the prior COVID-19 group (p < 0.05), whereas virgin B cells were more prevalent in the group without prior COVID-19 (p < 0.05), mature B cells predominated in both vaccinated groups (p < 0.01), and memory B cells, plasmablasts, early plasmablasts, and double-negative B cells were higher in the not vaccinated group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: BNT162b2 vaccine induces changes in B cell subpopulations, especially generating plasma cells and producing neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. However, the previous infection with SARS-CoV-2 does not significantly alter the dynamics of these subpopulations but induces more rapid and optimal antibody production.
Keywords: B cell; BNT162b2; SARS-CoV-2; immunophenotype; vaccine.
© 2022 Morales-Núñez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine and correlates of humoral immune responses and dynamics: a prospective, single-centre, longitudinal cohort study in health-care workers.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Sep;9(9):999-1009. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00220-4. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34224675 Free PMC article.
-
[Humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2 in workers of social health care centers of Castilla y León after vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine from Pfizer/Biontech.].Rev Esp Salud Publica. 2021 Oct 25;95:e202110141. Rev Esp Salud Publica. 2021. PMID: 34690347 Spanish.
-
Bimodal antibody-titer decline following BNT162b2 mRNA anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in healthcare workers of the INT - IRCCS "Fondazione Pascale" Cancer Center (Naples, Italy).Infect Agent Cancer. 2022 Jul 28;17(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13027-022-00451-1. Infect Agent Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35902961 Free PMC article.
-
Persistence of Immune Response in Health Care Workers After Two Doses BNT162b2 in a Longitudinal Observational Study.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 4;13:839922. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.839922. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35309303 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in the Humoral Immune Response Induced by the Administration of the BNT162b2 Pfizer/BioNTech Vaccine: A Systematic Review.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 7;10(6):909. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060909. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Profile Determines Response to Vaccination against COVID-19 in Kidney Transplant Recipients.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Oct 11;11(10):1583. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11101583. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37896986 Free PMC article.
-
Immune cell populations and induced immune responses at admission in patients hospitalized with vaccine breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 5;15:1360843. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1360843. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38903511 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor Binding Domain-Specific B Cell Memory Responses Among Individuals Vaccinated Against SARS-CoV-2.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;12(12):1396. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121396. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772064 Free PMC article.
-
Primary and Recall Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Breakthrough Infection.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Nov 9;11(11):1705. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11111705. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38006037 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination on B-Cell Phenotype in Systemic Sclerosis Patients.J Pers Med. 2022 Aug 31;12(9):1420. doi: 10.3390/jpm12091420. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36143205 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

