Synthesis and Discovery of Ligustrazine-Heterocycle Derivatives as Antitumor Agents
- PMID: 35958230
- PMCID: PMC9358002
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.941367
Synthesis and Discovery of Ligustrazine-Heterocycle Derivatives as Antitumor Agents
Abstract
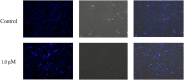
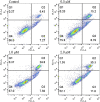
Ligustrazine (TMP) is a natural pyrazine alkaloid extracted from the roots of Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort, which has the potential as an antitumor agent. A series of 33 ligustrazine-heterocycle (TMPH) derivatives were designed, synthesized, and investigated via antitumor screening assays, molecular docking analysis, and prediction of drug-like properties. TMP was attached to other heterocyclic derivatives by an 8-12 methylene alkyl chain as a linker to obtain 33 TMPH derivatives. The structures were confirmed by 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, and high-resolution mass spectroscopy spectral (HR-MS) data. The antiproliferative activity against human breast cancer MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, mouse breast cancer 4T1, mouse fibroblast L929, and human umbilical vein endothelial HUVEC cell lines was evaluated by MTT assay. Compound 12-9 displayed significant inhibitory activity with IC50 values in the low micromolar range (0.84 ± 0.02 µM against the MDA-MB-231 cell line). The antitumor effects of compound 12-9 were further evaluated by plate cloning, Hoechst 33 342 staining, and annexin V-FITC/PI staining. The results indicated that compound 12-9 inhibited the proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Furthermore, molecular docking of compound 12-9 into the active site of the Bcl-2, CASP-3, and PSMB5 target proteins was performed to explore the probable binding mode. The 33 newly synthesized compounds were predicted to have good drug-like properties in a theoretical study. Overall, these results indicated that compound 12-9 inhibited cell proliferation through PSMB5 and apoptosis through Bcl-2/CASP-3 apoptotic signaling pathways and had good drug-like properties. These results provided more information, and key precursor lead derivatives, in the search for effective bioactive components from Chinese natural medicines.
Keywords: antitumor; apoptosis; ligustrazine–heterocyclic (TMPH) derivatives; proliferation; triple-negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Ma, Zhang, Hou, Liu, Wang, Lu, Zhu, Wei, Hong and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor CF declared a past collaboration with the author SM.
Figures


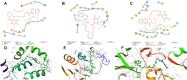
Similar articles
-
Novel Scopoletin Derivatives Kill Cancer Cells by Inducing Mitochondrial Depolarization and Apoptosis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(14):1774-1782. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666201207094416. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33292145
-
New thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine-based derivatives: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation as antiproliferative agents, EGFR and ARO inhibitors inducing apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Oct;115:105208. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105208. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34365057
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel ligustrazine-chalcone derivatives as potential anti-triple negative breast cancer agents.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Sep 1;47:128230. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128230. Epub 2021 Jun 27. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34186178
-
2-Anilinopyrimidine derivatives: Design, synthesis, in vitro anti-proliferative activity, EGFR and ARO inhibitory activity, cell cycle analysis and molecular docking study.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jun;99:103798. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103798. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32247112 Review.
-
Novel benzothiazole-based dual VEGFR-2/EGFR inhibitors targeting breast and liver cancers: Synthesis, cytotoxic activity, QSAR and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Feb 15;58:128529. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128529. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35007724 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of Chinese herbal medicine in the regulation of oxidative stress in treating hypertension: from therapeutics to mechanisms.Chin Med. 2024 Oct 29;19(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-01022-9. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39468572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An H., Heo J. S., Kim P., Lian Z., Lee S., Park J., et al. (2021). Tetraarsenic Hexoxide Enhances Generation of Mitochondrial ROS to Promote Pyroptosis by Inducing the Activation of Caspase-3/GSDME in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Death Dis. 12, 159. 10.1038/s41419-021-03454-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

