Vitamin D levels and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2 in children: A longitudinal cohort study
- PMID: 35958248
- PMCID: PMC9358048
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.960859
Vitamin D levels and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2 in children: A longitudinal cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the picture between vitamin D levels and clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2 in children.
Methods: A retrospective, longitudinal cohort study was performed. All included hospitalized cases were divided into the sufficient (sVD) and insufficient vitamin D (iVD) groups according to whether their serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] concentration was ≥30 ng/mL. Dynamic changes in clinical parameters were observed for seven time periods within 28 days after admission.
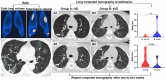
Results: Serum 25(OH)D concentrations were significantly negatively correlated with age in the included cases (r = -0.6; P < 0.001). Compared with the iVD group (n = 80), the sVD group (n = 36) had higher interleukin-6 (18.4 vs. 12.9; P = 0.003) within the first day; higher procalcitonin within the first (0.15 vs. 0.1; P = 0.03), 2-3 (0.14 vs. 0.07; P = 0.03), 4-5 (0.21 vs. 0.07; P = 0.02) days; more lymphocytes within the first (1.6 vs. 1.2; P = 0.02), 2-3 (3.7 vs. 2; P = 0.001), 4-5 (3.9 vs. 2.1; P = 0.01) and 6-7 (4.9 vs. 2.7; P = 0.02) days; notably, higher cycle threshold for N gene (30.6 vs 19.8; P = 0.03) or ORF1ab gene (31.4 vs 20.1; P = 0.03) within 2 to 3 days. Pneumonia lesions were found in eleven and six cases in the iVD and sVD groups, respectively, without significant difference on computed tomography at admission. Six out of eleven and five out of six had a repeat computed tomography after 1-2 weeks. Lesion improvement was more significant in the sVD group (P = 0.04).
Conclusions: Children with vitamin D insufficiency might have poorer clinical outcomes in Omicron subvariant BA.2 infection, especially in older pediatric patients. Further studies are needed to assess effectiveness of supplements in reducing the same.
Keywords: BA.2; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; children; subvariant; vitamin D.
Copyright © 2022 Peng, Huang, Liu, Gao and Liu.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of vitamin D status on adult COVID-19 pneumonia induced by Delta variant: A longitudinal, real-world cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 24;10:1121256. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1121256. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37035323 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and high-resolution computed tomography findings of 805 patients with mild or moderate infection from SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2.Curr Med Imaging. 2023 Apr 26. doi: 10.2174/1573405620666230426145140. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37170975
-
Characteristics of patients with non-severe infections of different SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariants in China.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 18;11:1511227. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1511227. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39744529 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world effectiveness of azvudine for patients infected with the SARS-CoV-2 omicron subvariant BA.5 in an intensive care unit.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Sep 28;15(9):4925-4937. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1093. Epub 2023 Sep 25. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37868850 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Omicron BA.2 Subvariant of SARS-CoV-2 Outcompetes BA.1 in Two Co-infection Cases.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 12;13:892682. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.892682. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35495156 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D and COVID-19: Narrative Review after 3 Years of Pandemic.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 20;14(22):4907. doi: 10.3390/nu14224907. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D: A key player in COVID-19 immunity and lessons from the pandemic to combat immune-evasive variants.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Dec;32(6):3631-3652. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01578-w. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39406981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of FokI rs2228570 and Tru9I rs757343 Polymorphisms in the Mortality of Patients Infected with Different Variants of SARS-CoV-2.Arch Med Res. 2023 Jun;54(4):310-318. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Arch Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37032232 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive effect of booster vaccination and vitamin D status on antibody production of Omicron variant-infected adults: A real-world cohort study.Clin Respir J. 2023 Oct;17(10):1067-1076. doi: 10.1111/crj.13694. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37675825 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of vitamin D status on adult COVID-19 pneumonia induced by Delta variant: A longitudinal, real-world cohort study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 24;10:1121256. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1121256. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37035323 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

