Comprehensive analysis of mutational profile and prognostic significance of complex glandular pattern in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 35958332
- PMCID: PMC9359943
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-22-127
Comprehensive analysis of mutational profile and prognostic significance of complex glandular pattern in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Complex glandular pattern (CGP) was included as high-grade pattern in the new grading system proposed by The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. We aimed to investigate the mutational profile and validate the prognostic significance and proper cut-off value to distinguish the aggressive behavior of CGP.
Methods: CGP was defined as nests of tumor cells with sieve-like perforation, fused glands with irregular borders or back-to-back glands without intervening stroma. Patients were categorized into four groups according to the percentage of CGP component (0%, 1-19%, 20-49%, 50-100%). Cox's proportional hazards model was applied to analyze recurrence free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).
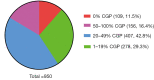
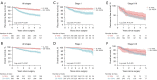
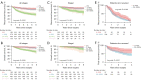
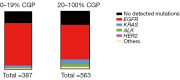
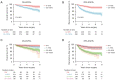
Results: A total of 950 patients with resected lung adenocarcinoma was enrolled. The most frequent driver mutation in this cohort was EGFR and was detected in 624 (65.7%) patients. EGFR mutation was more frequently observed in patients with <20% CGP than in patients with ≥20% CGP (73.6% vs. 60.2%), while KRAS mutation and ALK rearrangement was significantly associated with ≥20% CGP. Patients with 20% or greater CGP exhibited significant worse RFS (P<0.001) and OS (P<0.001) than their counterparts. Moreover, the multivariate Cox regression analysis confirmed that CGP (≥20%) was a risk factor for a worse RFS (P=0.001) and OS (P<0.001) independent of staging and gene mutation. Smaller portion of CGP (<20%) were comparable in RFS and OS to those without CGP (0%). There was also no significant difference in RFS and OS between the 20-49% and ≥50% group.
Conclusions: Our study provided mutational profile of patients with different CGP, validated CGP as a negative prognostic factor and provided extra evidences for the optimal cut-off value of CGP percentage.
Keywords: International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer grading system (IASLC grading system) grading system; complex glandular pattern (CGP); driver mutations; pulmonary adenocarcinoma.
2022 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-22-127/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Comment in
-
Complex glandular pattern as an independent predictor of survival probability in lung adenocarcinoma.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Sep;11(9):1739-1741. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-513. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36248342 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The prognostic value of Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog mutations in resected lung adenocarcinoma differs according to clinical features.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Jan;163(1):e73-e85. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.05.097. Epub 2020 Jun 21. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 32739163
-
High-grade tumor classified by new system is a prognostic predictor in resected lung adenocarcinoma.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 May;70(5):455-462. doi: 10.1007/s11748-021-01758-3. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 35050467
-
KRAS Mutation Is a Significant Prognostic Factor in Early-stage Lung Adenocarcinoma.Am J Surg Pathol. 2016 Dec;40(12):1579-1590. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000744. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27740967 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the novel International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer grading system in adenocarcinoma with spread through air space.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 31;13(8):1862-1876. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-265. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39263028 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational Profile and New IASLC/ATS/ERS Classification Provide Additional Prognostic Information about Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Study of 125 Patients from Brazil.Oncology. 2015;89(3):175-86. doi: 10.1159/000376552. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Oncology. 2015. PMID: 25833149
Cited by
-
A Comprehensive Evaluation of Clinicopathologic Characteristics, Molecular Features and Prognosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma with an Acinar Component.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 30;17(11):1825. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111825. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507306 Free PMC article.
-
The presence of a cribriform pattern is related to poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma after surgical resection: A meta-analysis.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2024 Sep;72(9):553-561. doi: 10.1007/s11748-024-02044-8. Epub 2024 May 27. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2024. PMID: 38801566 Review.
-
Integrating radiomics and deep learning for enhanced prediction of high-grade patterns in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):1076-1088. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-995. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40386715 Free PMC article.
-
Complex glandular pattern as an independent predictor of survival probability in lung adenocarcinoma.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Sep;11(9):1739-1741. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-513. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36248342 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kadota K, Kushida Y, Kagawa S, et al. Cribriform Subtype is an Independent Predictor of Recurrence and Survival After Adjustment for the Eighth Edition of TNM Staging System in Patients With Resected Lung Adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 2019;14:245-54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
