Forsythiasides: A review of the pharmacological effects
- PMID: 35958429
- PMCID: PMC9357976
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.971491
Forsythiasides: A review of the pharmacological effects
Abstract
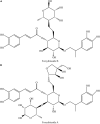
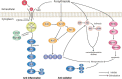
Forsythiasides are a kind of phenylethanol glycosides existing in Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl, which possesses extensive pharmacological activities. According to the different groups connected to the nucleus, forsythiasides can be divided into A-K. In recent years, numerous investigations have been carried out on forsythiasides A, B, C, D, E, and I, which have the effects of cardiovascular protection, anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, neuroprotection, et al. Mechanistically, forsythiasides regulate toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88)/nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB), nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and other signaling pathways, as well as the expression of related cytokines and kinases. Further exploration and development may unearth more treatment potential of forsythiasides and provide more evidence for their clinical applications. In summary, forsythiasides have high development and application value.
Keywords: Forsythia suspensa; anti-inflammation; anti-oxidation; cardiovascular protection; forsythiasides.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Liu, Zhou, Chen, An, Xing, Zhang, Jia and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory activity of the decoction of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl is related to Nrf2 and A20.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Dec 5;227:97-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.027. Epub 2018 Aug 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30145174
-
Phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and future research of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:318-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.040. Epub 2017 Sep 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28887216 Review.
-
Cryptotanshinone from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) inhibited inflammatory responses via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway.Chin Med. 2020 Mar 2;15:20. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00303-3. eCollection 2020. Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 32158495 Free PMC article.
-
Forsythiae Fructuse water extract attenuates liver fibrosis via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and TGF-β/smads signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Nov 15;262:113275. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113275. Epub 2020 Aug 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32810620
-
A review of pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties of Forsythiaside A.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Jul;169:105690. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105690. Epub 2021 May 23. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34029711 Review.
Cited by
-
Lithospermum erythrorhizon and Forsythia suspensa Prevent Collagen Degradation and Maintain Skin Hydration by Regulating MMPs and HAS2/HYAL1 Signaling.Molecules. 2025 Feb 27;30(5):1083. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051083. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076307 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis and Alzheimer's: unveiling new avenues for the treatment and prevention.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Apr 1;40(4):167. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01587-w. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40167846 Review.
-
Phillyrin prevents sepsis-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting the NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis signaling pathway.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Oct 10;57(3):447-462. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024161. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 39394820 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolome Profiling of Marrubium peregrinum L. and Marrubium friwaldskyanum Boiss Reveals Their Potential as Sources of Plant-Based Pharmaceuticals.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 1;24(23):17035. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317035. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069358 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly and analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl.BMC Genomics. 2023 Nov 23;24(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09821-4. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37996801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu J, Ma L, Zhang J, Xu C. Research progress of Forsythia suspensa. Cent South Pharm. (2012) 10:760–4.
-
- Xia W, Dong C, Yang C, Chen H. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacology of Forsythia suspensa. Mod Chin Med. (2016) 18:1670–4. 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.2016.12.031 - DOI
-
- Zhang T, Shi L, Liu W, Zhang M, Yang J, Li F. research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Forsythia. J Liaoning U Tradit Chinese Med. (2016) 18:222–4. 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2016.12.067 - DOI
-
- Wei Q, Li P, Wu T, Li C, Zhang R. Progress in phenylethanoid glycosides from Forsythia suspensa. Chin J Clin Pharmacol. (2018) 34:2481–5. 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2018.20.024 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources