Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on improvement of quality of life after super-miniPCNL and risk analysis for postoperative complications
- PMID: 35958457
- PMCID: PMC9360903
Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on improvement of quality of life after super-miniPCNL and risk analysis for postoperative complications
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on the improvement of quality of life after super-miniPCNL (SMP) and the risk analysis of postoperative complications.
Methods: The clinical data of 124 SMP patients who were admitted from February 2019 to February 2021 were analyzed retrospectively. Thereinto, 58 cases received routine nursing were regarded as the control group (CG), and 66 received rapid rehabilitation nursing were considered as the observation group (OG). The negative emotions, pain relief, incidence of complications and quality of life were compared. In view of the occurrence of complications, patients were divided into complication group and non-complication group, and the risk factors were assessed by logistics regression.
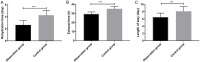
Results: The time of fluid infusion, exhaust, defecation and hospitalization in the OG were shorter than those in the CG, and the difference was statistically remarkable (P<0.05). In the OG, the SF-36 and score of postoperative quality of life were obviously higher (P<0.05), while the postoperative visual analogue scale (VAS), self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and self-rating depression scale (SDS) were markedly lower. Logistics regression analysis manifested that the operation time, course of disease, stone residue, history of preoperative infection and nursing plan were independently correlated with complications.
Conclusion: Rapid rehabilitation nursing for SMP patients is beneficial to accelerating postoperative recovery, reducing the occurrence of complications and improving quality of life.
Keywords: Rapid rehabilitation nursing; kidney stone; quality of life; risk analysis; super-miniPCNL.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-quality nursing can reduce the incidence of adverse events in esophageal cancer patients after operation in the intensive care unit and improve postoperative rehabilitation.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):11851-11859. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34786114 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of high-quality nursing intervention on negative emotions, postoperative complications and gastrointestinal function in patients with gastric cancer surgery.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Mar 15;14(3):1652-1662. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35422953 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on inflammation and liver function after laparoscopic radical resection of primary liver cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Nov 15;14(11):8156-8165. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 36505328 Free PMC article.
-
Specific nursing improves postoperative urine control function and the self-efficacy of patients undergoing radical prostatectomies.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Mar 15;14(3):1695-1704. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35422910 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of early rehabilitation nursing on postoperative rehabilitation of patients with hallux valgus based on information-motivation-behavior skills model.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Jan;41(1):235-241. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.1.9791. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39867770 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive and continuous nursing strategies in perioperative management of upper urinary tract stones treated with holmium laser lithotripsy.BMC Urol. 2025 Jul 14;25(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12894-025-01850-3. BMC Urol. 2025. PMID: 40660146 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy of precision liver resection for primary liver cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Mar 15;16(3):897-904. doi: 10.62347/QBBO2532. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38586102 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Towards Rehabilitation in Patients with Breast Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 Mar 12;18:1483-1492. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S486270. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40099046 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the application of Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) in elderly patients undergoing surgery for kidney stones.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):1711-1720. doi: 10.62347/QOAR2593. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoffman A, Braun MM, Khayat M. Kidney disease: kidney stones. FP Essent. 2021;509:33–38. - PubMed
-
- Scarcella S, Tiroli M, Torino G, Mariscoli F, Cobellis G, Galosi AB. Combined treatment of ureteropelvic junction obstruction and renal calculi with robot-assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty and laser lithotripsy in children: case report and non-systematic review of the literature. Int J Med Robot. 2021;17:e2246. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
