The effect and mechanism of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on angiogenesis in a rat model of chronic myocardial ischemia
- PMID: 35958466
- PMCID: PMC9360859
The effect and mechanism of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on angiogenesis in a rat model of chronic myocardial ischemia
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effect of dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) on angiogenesis and its underlying mechanism in a rat model of chronic myocardial ischemia (CMI).
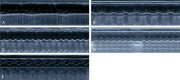
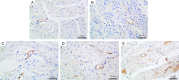
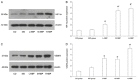
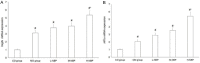
Methods: Forty Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into four groups: model, low-dose NBP (L-NBP), middle-dose NBP (M-NBP), or high-dose NBP (H-NBP) (n=10/group). All groups received intraperitoneal injections of isoprinosine hydrochloride daily for 14 days. Additionally, the L-NBP, M-NBP, and H-NBP groups received NBP at 3, 6, and 12 mg per kg body weight, respectively, by intraperitoneal injection. An additional 10 rats (control group) received 0.9% sodium chloride via intraperitoneal injection for 14 consecutive days. Echocardiography was used for the measurement of heart function. Immunohistochemical staining for factor VIII-related antigen and microvascular density determination were performed. The protein and mRNA expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in CMI areas were measured by western blot and RT-PCR, respectively.
Results: Electrocardiograms showed that NBP improved cardiac function by regulating left ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic diameters, ejection fraction, and fractional shortening. Compared with the control and model groups, the L-NBP, M-NBP, and H-NBP groups showed increased mRNA and protein expression of VEGFA and HIF-1α in myocardial tissue. The mRNA and protein expression of VEGFA and HIF-α in the H-NBP group were the highest.
Conclusion: NBP treatment promotes VEGF and HIF-1α protein expression during myocardial ischemia, which may represent useful biomarkers for coronary collateral establishment and offer potential targets for therapeutic induction of angiogenesis in patients with CMI.
Keywords: Dl-3-n-butylphthalide; angiogenesis; chronic myocardial ischemia; hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α; vascular endothelial growth factor.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture pretreatment promotes angiogenesis via hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and vascular endothelial growth factor in a rat model of chronic myocardial ischemia.Acupunct Med. 2021 Aug;39(4):367-375. doi: 10.1177/0964528420938378. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Acupunct Med. 2021. PMID: 32811184
-
Dl-3-N-Butylphthalide Attenuates Hypoxic Injury of Neural Stem Cells by Increasing Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022 Feb;31(2):106221. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.106221. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022. PMID: 34837757
-
Dl-3-N-butylphthalide promotes angiogenesis and upregulates sonic hedgehog expression after cerebral ischemia in rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Jun;25(6):748-758. doi: 10.1111/cns.13104. Epub 2019 Feb 19. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 30784219 Free PMC article.
-
Dl-NBP (Dl-3-N-Butylphthalide) Treatment Promotes Neurological Functional Recovery Accompanied by the Upregulation of White Matter Integrity and HIF-1α/VEGF/Notch/Dll4 Expression.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 24;10:1595. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01595. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32038259 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced angiogenesis with dl-3n-butylphthalide treatment after focal cerebral ischemia in RHRSP.Brain Res. 2009 Sep 15;1289:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.06.018. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19524555
Cited by
-
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide promotes angiogenesis in ischemic stroke mice through upregulating autocrine and paracrine sonic hedgehog.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023 Dec;44(12):2404-2417. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01137-z. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023. PMID: 37580491 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Neuroprotective Mechanisms of G-3702 in Ischemic Stroke via Integrated Metabolomics and Computational Approaches.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Apr;31(4):e70352. doi: 10.1111/cns.70352. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40265291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moroni F, Gertz Z, Azzalini L. Relief of ischemia in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021;23:80. - PubMed
-
- Fu YM, Li J, Wu S, Wang H. Electroacupuncture pretreatment promotes angiogenesis via hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and vascular endothelial growth factor in a rat model of chronic myocardial ischemia. Acupunct Med. 2021;39:367–375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
