Establishment and validation of a nomogram that predicts the risk of type 2 diabetes in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal observational study
- PMID: 35958467
- PMCID: PMC9360847
Establishment and validation of a nomogram that predicts the risk of type 2 diabetes in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a longitudinal observational study
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to establish and validate a nomogram for better assessment of the risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) based on independent predictors.
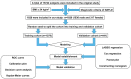
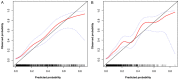
Methods: Of 1820 eligible participants from the NAGALA cohort enrolled in the study. Multivariate Cox regression was employed to construct the nomogram. The performance was assessed by area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), C-index, calibration curve, decision curve analysis, and Kaplan-Meier analysis.
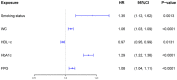
Results: Five predictors were selected from 17 variables. The AUC values at different time points all indicated that the model constructed with these five predictors had good predictive power. Decision curves indicated that the model could be applied to clinical applications.
Conclusions: We established and validated a reasonable, economical nomogram for predicting the risk of T2D in obese NAFLD patients. This simple clinical tool can help with risk stratification and thus contribute to the development of effective prevention programs against T2D in obese patients with NAFLD.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes; cohort study; nomogram; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A Prediction Model Based on Noninvasive Indicators to Predict the 8-Year Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study.Biomed Res Int. 2021 May 14;2021:5527460. doi: 10.1155/2021/5527460. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34095297 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a Novel Prediction Model for Predicting 2-Year Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the Non-Obese Population with Normal Blood Lipid Levels: A Large Prospective Cohort Study from China.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Jun 28;14:2909-2922. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S319759. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34234521 Free PMC article.
-
Derivation and Validation of a Prediction Model for Predicting the 5-Year Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes in Non-Obese Adults: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 May 11;14:2087-2101. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S304994. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 34007195 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the non-obese Chinese population.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Oct 15;12(10):6149-6159. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33194020 Free PMC article.
-
A Prediction Model of the Incidence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease With Visceral Fatty Obesity: A General Population-Based Study.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 23;10:895045. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.895045. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35812496 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Relationship Between Plasma Aldosterone Concentrations and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosis in Patients with Hypertension: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Jun 6;16:1625-1636. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S408722. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37304667 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the C-reactive protein-triglyceride glucose index in predicting the risk of new-onset diabetes in the general population aged 45 years and older: a national prospective cohort study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 May 9;25(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01947-8. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40346472 Free PMC article.
-
Association of white blood cell count to mean platelet volume ratio with type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a Chinese population: a cross-sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Jul 29;24(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01644-y. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39075499 Free PMC article.
-
Association between circadian syndrome and MASLD risk: evidence from a large cross-sectional study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 May 21;25(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03997-7. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40399801 Free PMC article.
-
Associating plasma aldosterone concentration with the prevalence of MAFLD in hypertensive patients: insights from a large-scale cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 19;15:1451383. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1451383. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39363897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14:88–98. - PubMed
-
- Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Samocha-Bonet D, Debs S, Greenfield JR. Prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes: a pathophysiological-based approach. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29:370–379. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
