Effect of proximal femoral nail antirotation on clinical outcome, inflammatory factors and myocardial injury markers in patients with femoral trochanteric fracture
- PMID: 35958501
- PMCID: PMC9360835
Effect of proximal femoral nail antirotation on clinical outcome, inflammatory factors and myocardial injury markers in patients with femoral trochanteric fracture
Abstract
Objective: To compare the differences between proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) and dynamic hip screw (DHS) in treatment of femoral trochanteric fracture and analyze the factors influencing recovery after PFNA treatment.
Methods: Eighty-six patients with femoral trochanteric fracture admitted to Taizhou Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine between January 2019 and June 2021 were enrolled in the study and assigned into a PFNA group and DHS group (n=43 in each group) before undergoing these treatments. The clinical efficacy, inflammatory factors, and myocardial injury markers were compared between the two groups. The influencing factors on recovery after PFNA treatment were analyzed by univariate and multivariate analysis.
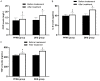
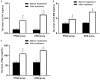
Results: Compared to the DHS group, the PFNA group had shorter surgical time, length of stay in hospital, postoperative weight-bearing time, time of healing and detumescence, and less intraoperative blood loss (all P<0.001). The incidence of post-surgical complications with PFNA was lower than with DHS (P<0.05). The serum levels of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein and tumor necrosis factor-αof the PFNA group were lower than those of the DHS group (all P<0.05). Moreover, the serum levels of cardiac troponin T, creatine kinase-MB and myoglobin in the PFNA group were also lower than for the DHS (all P<0.05). At the first, third, and sixth months after surgery, the Harris scores for PFNA were higher than for DHS (all P<0.05). The univariate and multivariate analysis showed that instability of fracture, history of osteoporosis, excessive intraoperative bleeding, poor compliance with rehabilitation exercise, and long time from injury to surgery were risk factors for poor recovery following PFNA treatment for patients with femoral trochanteric fracture.
Conclusion: Compared to DHS, PFNA had better clinical efficacy and gave lower serum levels of inflammatory factors and myocardial injury markers. Fracture classification, history of osteoporosis, intraoperative amount of bleeding, compliance of rehabilitation exercise, and time from injury to surgery were closely associated with recovery following PFNA treatment.
Keywords: Femoral intertrochanteric fracture; dynamic hip screw; proximal femoral nail antirotation; recovery effects; risk factors.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of efficacy, complications and TGF-β2 expression between DHS and PFNA in elderly patients with osteoporotic femoral intertrochanteric fracture.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jul;16(1):394-399. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6177. Epub 2018 May 17. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29896265 Free PMC article.
-
[Effectiveness comparison of proximal femoral nail antirotation and dynamic hip screw for intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly patients].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Jun;26(6):671-4. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22792760 Chinese.
-
Comparison of the Clinical Effectiveness of PFNA, PFLCP, and DHS in Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture.Am J Ther. 2017 Nov/Dec;24(6):e659-e666. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000346. Am J Ther. 2017. PMID: 26488362 Clinical Trial.
-
A Retrospective Study of 98 Elderly Patients with High-Risk Lateral Femoral Wall Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures to Compare Outcomes Following Surgery with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) Versus Dynamic Hip Screw (DHS).Med Sci Monit. 2022 Aug 17;28:e936923. doi: 10.12659/MSM.936923. Med Sci Monit. 2022. PMID: 35974685 Free PMC article.
-
Antirotation proximal femoral nail versus dynamic hip screw for intertrochanteric fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013 Jun;99(4):377-83. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2012.12.019. Epub 2013 May 23. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23707739 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors for excessive lateral migration of the blade in proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in elderly patients with intertrochanteric femur fracture.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):5637-5648. doi: 10.62347/PSAA8681. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39544750 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the therapeutic efficacy of hip arthroplasty and proximal femoral nail antirotation internal fixation for unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):3690-3701. doi: 10.62347/RMSY6686. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39262734 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in nail position and antirotation blade angles on the risk of femoral head varus in PFNA fixed patients: a clinical review and comprehensive biomechanical research.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jun 18;29(1):336. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01892-7. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38890700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schipper IB, Steyerberg EW, Castelein RM, van der Heijden FH, den Hoed PT, Kerver AJ, van Vugt AB. Treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Randomised comparison of the gamma nail and the proximal femoral nail. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86:86–94. - PubMed
-
- Yano S, Matsuura Y, Hagiwara S, Nakamura J, Kawarai Y, Suzuki T, Kanno K, Shoda J, Tsurumi Y, Ohtori S. Determinants of fracture type in the proximal femur: biomechanical study of fresh frozen cadavers and finite element models. Bone. 2022;158:116352. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
