Phosphatidylserine-exposed red blood cells and ineffective erythropoiesis biomarkers in patients with thalassemia
- PMID: 35958503
- PMCID: PMC9360869
Phosphatidylserine-exposed red blood cells and ineffective erythropoiesis biomarkers in patients with thalassemia
Abstract
Objective: The degree of ineffective erythropoiesis is known to be associated with clinical severity among individuals with thalassemia. The association of ineffective erythropoiesis biomarker levels with different thalassemia genotypes, however, remains limited. The aim of this study was to explore the level of phosphatidylserine-exposed red blood cells (PS-exposed RBCs) and ineffective erythropoiesis biomarkers (growth-differentiation factor-15 and soluble transferrin receptors) in patients with different genotypes.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted on 139 patients of age 18 years and above with different genotypes at Srinagarind Hospital, Khon Kaen University, Thailand. The levels of PS-exposed RBCs were determined using flow cytometry. Measurements of growth-differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) and soluble transferrin receptors (sTfR) were evaluated by the ELISA method.
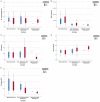
Results: The PS-exposed RBCs levels were found to be significantly higher in splenectomized beta-thalassemia patients. Patients with beta-thalassemia had the highest GDF-15 levels, followed by patients with non-deletional alpha-thalassemia. Patients with non-deletional alpha-thalassemia showed elevated hemoglobin levels and reduced GDF-15 levels after splenectomy. Patients with beta-thalassemia and non-deletional alpha-thalassemia had the highest levels of PS-exposed RBCs and ineffective erythropoiesis biomarkers, which correlated with the clinical severity of thalassemia.
Conclusions: The levels of ineffective erythropoiesis biomarkers were different across thalassemia genotypes. Splenectomy may improve clinical symptoms of patients with non-deletional alpha thalassemia but not of patients with beta-thalassemia. These findings demonstrate differences in the degree of ineffective erythropoiesis in thalassemia, which emphasizes the need for different treatment approaches among patients with different thalassemia genotypes.
Keywords: Phosphatidylserine exposed red blood cells; ineffective erythropoiesis biomarkers; thalassemia.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Imbalance of erythropoiesis and iron metabolism in patients with thalassemia.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jan 1;16(2):302-310. doi: 10.7150/ijms.27829. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30745811 Free PMC article.
-
Erythroid bone marrow activity and red cell hemoglobinization in iron sufficient beta-thalassemia heterozygotes as reflected by soluble transferrin receptor and reticulocyte hemoglobin in content. Correlation with genotypes and Hb A(2) levels.Haematologica. 2003 Jun;88(6):631-6. Haematologica. 2003. PMID: 12801838
-
Nucleated red blood cells and soluble transferrin receptor in thalassemia syndromes: relationship with global and ineffective erythropoiesis.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47(12):1539-42. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2009.340. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19824799
-
Pathogenic Mechanisms in Thalassemia I: Ineffective Erythropoiesis and Hypercoagulability.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2023 Apr;37(2):341-351. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2022.12.005. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2023. PMID: 36907607 Review.
-
What can we learn from ineffective erythropoiesis in thalassemia?Blood Rev. 2018 Mar;32(2):130-143. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Blood Rev. 2018. PMID: 29054350 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CETP gene polymorphisms and haplotypes are explanatory variables for HDL cholesterol level in sickle cell disease.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024 Jan 22;57:e12879. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2023e12879. eCollection 2024. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2024. PMID: 38265339 Free PMC article.
-
Measures of cellular oxidative damage following vitamin E supplementation in young patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemia: a double-blind randomized controlled trial.BMC Pediatr. 2025 May 20;25(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s12887-025-05741-2. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40389864 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Importance of CD71+ Erythrocyte Cell Levels in Prognosis in Patients With β-Thalassemia.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Jun;38(11-12):e25084. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25084. Epub 2024 Jun 26. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 38924171 Free PMC article.
-
Detection and clinical application of red blood cell survival.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Mar 28;49(3):476-481. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.230405. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38970522 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese, English.
-
Deciphering and disrupting PIEZO1-TMEM16F interplay in hereditary xerocytosis.Blood. 2024 Jan 25;143(4):357-369. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023021465. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38033286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borenstain-Ben Yashar V, Barenholz Y, Hy-Am E, Rachmilewitz EA, Eldor A. Phosphatidylserine in the outer leaflet of red blood cells from beta-thalassemia patients may explain the chronic hypercoagulable state and thrombotic episodes. Am J Hematol. 1993;44:63–65. - PubMed
-
- Taher AT, Otrock ZK, Uthman I, Cappellini MD. Thalassemia and hypercoagulability. Blood Rev. 2008;22:283–292. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
