Development of mouse model for oral allergy syndrome to identify IgE cross-reactive pollen and food allergens: ragweed pollen cross-reacts with fennel and black pepper
- PMID: 35958602
- PMCID: PMC9358994
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.945222
Development of mouse model for oral allergy syndrome to identify IgE cross-reactive pollen and food allergens: ragweed pollen cross-reacts with fennel and black pepper
Abstract
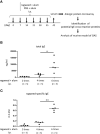
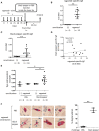
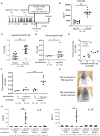
Oral allergy syndrome (OAS) is an IgE-mediated immediate food allergy that is localized to the oral mucosa. Pollen food allergy syndrome (PFAS), a pollinosis-associated OAS, is caused by cross-reactivity between food and pollen allergens. However, we need to more precisely understand the underlying pathogenesis of OAS/PFAS. In the present study, we developed a method to comprehensively identify cross-reactive allergens by using murine model of OAS and protein microarray technology. We focused on lip angioedema, which is one of the most common symptoms of OAS, and confirmed that mast cells reside in the tissues inside the lower lip of the mice. Interestingly, when the food allergen ovalbumin (OVA) was injected inside the lower lip of mice with high levels of OVA-specific IgE followed by an intravenous injection of the Evans blue dye, we found immediate dye extravasation in the skin of the neck in a mast cell-dependent manner. In addition, the degree of mast cell degranulation in the oral cavity, reflecting the severity of oral allergic responses, can be estimated by measuring the amount of extravasated dye in the skin. Therefore, we used this model of OAS to examine IgE cross-reactive allergens in vivo. Protein microarray analysis showed that serum IgE from mice intraperitoneally sensitized with ragweed pollen, one of the major pollens causing pollinosis, bound highly to protein extracts from several edible plants including black peppercorn and fennel. We confirmed that the levels of black pepper-specific IgE and fennel-specific IgE were significantly higher in the serum from ragweed pollen-sensitized mice than in the serum from non-sensitized control mice. Importantly, analysis of murine model of OAS showed that the injection of black pepper or fennel extract induced apparent oral allergic responses in ragweed pollen-sensitized mice. These results indicate IgE cross-reactivity of ragweed pollen with black pepper and fennel. In conclusion, we developed mouse model of OAS to identify IgE cross-reactive pollen and food allergens, which will help understand the pathogenesis of OAS/PFAS.
Keywords: IgE; allergen; cross-reactivity; food; mouse model; oral allergy syndrome (OAS); pollen.
Copyright © 2022 Kamei, Izawa, Ando, Kaitani, Yamamoto, Maehara, Ide, Yamada, Kojima, Wang, Tokushige, Nakano, Shimizu, Ogawa, Okumura and Kitaura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mugwort-fennel-allergy-syndrome associated with sensitization to an allergen homologous to Api g 5.Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Aug 1;45(4):130-7. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24067338
-
Epidemiological study of oral allergy syndrome in birch pollen dispersal-free regions.Allergol Int. 2020 Apr;69(2):246-252. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2019.09.008. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Allergol Int. 2020. PMID: 31708436
-
Oral allergy syndrome in patients with airborne pollen allergy treated with specific immunotherapy.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2008;16(1):19-24. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2008. PMID: 18358104
-
Oral allergy syndrome.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018 Jan 1;32(1):27-30. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2018.32.4489. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29336286 Review.
-
[Cross-reactivity between fruit and vegetables].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2003 May-Jun;31(3):141-6. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0546(03)79281-7. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2003. PMID: 12783764 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus δ-toxin present on skin promotes the development of food allergy in a murine model.Front Immunol. 2023 May 19;14:1173069. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1173069. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37275864 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal administration of ceramide liposome suppresses allergic rhinitis by targeting CD300f in murine models.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 10;14(1):8398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58923-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38600251 Free PMC article.
-
Murine model identifies tropomyosin as IgE cross-reactive protein between house dust mite and coho salmon that possibly contributes to the development of salmon allergy.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 30;14:1238297. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1238297. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37711608 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal substance P-driven MRGPRX2-dependent mast cell degranulation products differentially promote vascular permeability.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 21;15:1477072. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1477072. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39640264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ebisawa M, Ito K, Fujisawa T. Committee for Japanese pediatric guideline for food allergy, the Japanese society of pediatric allergy and clinical immunology, the Japanese society of allergology. Japanese guidelines for food allergy 2017. Allergol Int (2017) 66(2):248–64. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2017.02.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

