Immunomodulatory roles of selenium nanoparticles: Novel arts for potential immunotherapy strategy development
- PMID: 35958612
- PMCID: PMC9361286
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.956181
Immunomodulatory roles of selenium nanoparticles: Novel arts for potential immunotherapy strategy development
Abstract
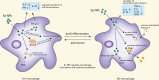
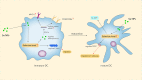
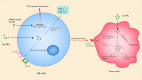
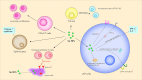
Current chemotherapy strategies used in clinic appear with lots of disadvantages due to the low targeting effects of drugs and strong side effects, which significantly restricts the drug potency, causes multiple dysfunctions in the body, and even drives the emergence of diseases. Immunotherapy has been proved to boost the body's innate and adaptive defenses for more effective disease control and treatment. As a trace element, selenium plays vital roles in human health by regulating the antioxidant defense, enzyme activity, and immune response through various specific pathways. Profiting from novel nanotechnology, selenium nanoparticles have been widely developed to reveal great potential in anticancer, antibacterial, and anti-inflammation treatments. More interestingly, increasing evidence has also shown that functional selenium nanoparticles can be applied for potential immunotherapy, which would achieve more effective treatment efficiency as adjunctive therapy strategies for the current chemotherapy. By directly interacting with innate immune cells, such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells, selenium nanoparticles can regulate innate immunity to intervene disease developments, which were reported to boost the anticancer, anti-infection, and anti-inflammation treatments. Moreover, selenium nanoparticles can also activate and recover different T cells for adaptive immunity regulations to enhance their cytotoxic to combat cancer cells, indicating the potential of selenium nanoparticles for potential immunotherapy strategy development. Here, aiming to enhance our understanding of the potential immunotherapy strategy development based on Se NPs, this review will summarize the immunological regulation effects of selenium nanoparticles and the application of selenium nanoparticle-based immunotherapy strategies. Furthermore, we will discuss the advancing perspective of selenium nanoparticle-based potential immunotherapy as a kind of novel adjunctive therapy to enhance the efficiency of current chemotherapies and also introduce the current obstacles for the development of selenium nanoparticles for potential immunotherapy strategy development. This work is expected to promote the future research on selenium nanoparticle-assisted immunotherapy and finally benefit the more effective disease treatments against the threatening cancer and infectious and chronic diseases.
Keywords: NK cells; Selenium nanoparticles; T cells; immunotherapy; macrophages.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Yang, Fan, Jin, Liao, Li, Liu, Liang, Zhang, Xu and Pi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Advancing of Selenium Nanoparticles Against Infectious Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 30;12:682284. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.682284. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34393776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium-Containing Nanoparticles Combine the NK Cells Mediated Immunotherapy with Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy.Adv Mater. 2020 Mar;32(12):e1907568. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907568. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 32053267
-
Selenium-containing ruthenium complex synergizes with natural killer cells to enhance immunotherapy against prostate cancer via activating TRAIL/FasL signaling.Biomaterials. 2019 Oct;219:119377. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119377. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 31374478
-
[Development of antituberculous drugs: current status and future prospects].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):753-74. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240921 Review. Japanese.
-
Nanotechnology-based manipulation of dendritic cells for enhanced immunotherapy strategies.Nanomedicine. 2010 Aug;6(4):523-9. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Nanomedicine. 2010. PMID: 20085824 Review.
Cited by
-
A Snapshot of Selenium-enclosed Nanoparticles for the Management of Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(11):841-858. doi: 10.2174/0113816128297329240305071103. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38462835 Review.
-
Unveiling the potential anticancer activity of Spirulina maxima extract-nanoemulsion through in vitro and in vivo studies.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 6;15(1):912. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82924-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39762303 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond anti-inflammatory strategies: addressing immunosuppression with nanomaterials in sepsis treatment.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 18;15:1500734. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1500734. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39624087 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Drug Delivery Systems in Regenerative Medicine: An Updated Review.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 18;15(2):695. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020695. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36840018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Nanoparticle-Conjugates and Nanotheranostics in Abrogating Oxidative Stress and Ameliorating Neuroinflammation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 18;12(10):1877. doi: 10.3390/antiox12101877. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37891956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dominguez-Ramirez L, Rodriguez-Perez F, Sosa-Jurado F, Santos-Lopez G, Cortes-Hernandez P. The role of metabolic comorbidity in COVID-19 mortality of middle-aged adults. The case of Mexico. medRxiv (2020), 20244160. doi: 10.1101/2020.12.15.20244160 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

