MiR-365-3p is a negative regulator in IL-17-mediated asthmatic inflammation
- PMID: 35958620
- PMCID: PMC9361323
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.953714
MiR-365-3p is a negative regulator in IL-17-mediated asthmatic inflammation
Abstract
Background: Interleukin-17, the major proinflammatory cytokine secreted by Th17 cells, makes essential contribution to pathogenesis of severe asthma, while the detailed mechanisms, especially the involvement of microRNAs which are also important participants in asthma progression, remains largely unclear.
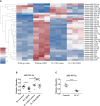
Methods: In this study, we established a house dust mite (HDM) extract-induced murine asthmatic models and the miRNA expression in the lung tissues of mice were profiled by miRNA microarray assay. The effect of miR-365-3p on IL-17-mediated inflammation was examined by qRT-PCR and immunoblotting analysis. The involvement of ARRB2 as target gene of miR-365-3p was verified by overexpression or RNA interference.
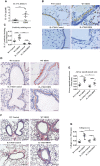
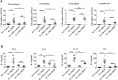
Results: HDM extract-induced asthmatic inflammation was proved to be IL17-mediated and miR-365-3p was screened out to be the only miRNA exclusively responsive to IL-17. miR-365-3p, whose expression was significantly downregulated upon IL-17 stimulation, was demonstrated to exert remarkable anti-inflammatory effect to decrease IL-17-provoked inflammatory cytokines (KC/IL-8 and IL-6) in both airway epithelial cells and macrophages of murine and human origins, verifying its universal antagonizing activity against IL-17-initiated inflammation across the two species. ARRB2 was characterized as the key target of miR-365-3p to negate IL-17-induced inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: Taken together, our data supported the notion that miR-365-3p, which was diminished by IL-17 in murine and human asthmatic pathogenesis, functioned as an essential negative mediator in IL-17-stimuated inflammatory response by targeting ARRB2, which would shed new light to the understanding and therapeutics thereof of asthmatic inflammation.
Keywords: ARRB2; IL-17KO; IL-8; asthma; miR-365-3p.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Li, Fan, Qu, Shang, Qin, Xu, Hamid, Dang, Chang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Xuanhong Dingchuan Tang suppresses bronchial asthma inflammation via the microRNA-107-3p/PTGS2/MAPK axis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Dec 20;25(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01506-9. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39704779
-
Divergent Roles of miR-3162-3p in Pulmonary Inflammation in Normal and Asthmatic Mice as well as Antagonism of miR-3162-3p in Asthma Treatment.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2020;181(8):594-605. doi: 10.1159/000507250. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32610326
-
Salidroside Attenuates Airway Inflammation and Remodeling via the miR-323-3p/SOCS5 Axis in Asthmatic Mice.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022;183(4):424-434. doi: 10.1159/000520444. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34856542
-
Mechanism of miR-130b-3p in relieving airway inflammation in asthma through HMGB1-TLR4-DRP1 axis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Dec 20;82(1):9. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05529-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39704848 Free PMC article.
-
Asthma inflammatory phenotypes show differential microRNA expression in sputum.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 May;137(5):1433-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.02.018. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27155035
Cited by
-
Xuanhong Dingchuan Tang suppresses bronchial asthma inflammation via the microRNA-107-3p/PTGS2/MAPK axis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Dec 20;25(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01506-9. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39704779
-
Circulating miRNA expression in extracellular vesicles is associated with specific injuries after multiple trauma and surgical invasiveness.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 23;14:1273612. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273612. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37936707 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring miRNA therapies and gut microbiome-enhanced CAR-T cells: advancing frontiers in glioblastoma stem cell targeting.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar;398(3):2169-2207. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03479-9. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39382681 Review.
-
Nonspecific Orbital Inflammation (NSOI): Unraveling the Molecular Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Modalities, and Therapeutic Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 26;25(3):1553. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031553. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in microRNAs during Storage and Processing of Breast Milk.Metabolites. 2023 Jan 17;13(2):139. doi: 10.3390/metabo13020139. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36837760 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

