The promising role of probiotics/prebiotics/synbiotics in energy metabolism biomarkers in patients with NAFLD: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35958869
- PMCID: PMC9358257
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.862266
The promising role of probiotics/prebiotics/synbiotics in energy metabolism biomarkers in patients with NAFLD: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a chronic liver disease with a high prevalence worldwide, seriously harming human health, and its pathogenesis remains unclear. In recent years, increasing evidence has indicated that intestinal microbiota plays an important role in the occurrence and development of NAFLD. The regulation method of probiotics/prebiotics/synbiotics can alter the intestinal microbiota and has been suggested as an option in the treatment of NAFLD.
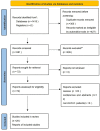
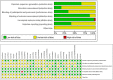
Methods: Five databases of PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, clinicaltrails.gov, and China National Knowledge Infrastructure were searched initially, and then the eligible studies were screened. Finally, the data of included studieswere extracted, combined and analyzed.
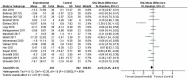
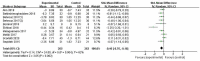
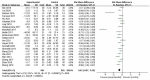
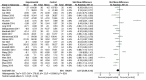
Results: A total of 29 randomized controlled trials involving 2,110 patients were included in this study. The results showed that using probiotics/prebiotics/synbiotics in the intervention group could reduce the levels of glucose (SMD = -0.23, 95% CI [-0.45, -0.01], P = 0.04), HOMA-IR (SMD = -0.47, 95% CI [-0.63, -0.31], P < 0.00001) and insulin (SMD = -0.46, 95% CI [-0.76, -0.16], P = 0.002) in sugar metabolism; in terms of lipid metabolism, the levels of TC (SMD = -0.62, 95%CI [-0.87, -0.36], P < 0.00001), and LDL-C (SMD = -0.57, 95%CI [-0.85, -0.28], P < 0.00001) were decreased; and the level of ALB was decreased in protein metabolism (SMD = -0.34, 95%CI [-0.61, -0.06], P = 0.02).
Conclusions: Based on the current evidence, probiotics/prebiotics/synbiotics may improve energy metabolism biomarkers in the NAFLD population, but these effects still need to be confirmed by further research.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/#aboutpage.
Keywords: NAFLD; energy metabolism biomarkers; microbiota modulation; prebiotics; probiotics; synbiotics.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Liu, Wang, Duan, Jia, Chen and Li.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Efficacy of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on liver enzymes, lipid profiles, and inflammation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 22;24(1):283. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03356-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39174901 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of probiotics and synbiotics on patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An umbrella study on meta-analyses.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023 Oct;57:475-486. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.07.087. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023. PMID: 37739694
-
The effect of gut microbiome-targeted therapies in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 6;11:1470185. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1470185. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39834471 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics for the improvement of metabolic profiles in patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(4):577-598. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1740645. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32329633
-
The impact of gut microbiome-targeted therapy on liver enzymes in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: an umbrella meta-analysis.Nutr Rev. 2024 May 10;82(6):815-830. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad086. Nutr Rev. 2024. PMID: 37550264
Cited by
-
Prebiotic Treatment in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)-A Randomized Pilot Trial.Nutrients. 2024 May 22;16(11):1571. doi: 10.3390/nu16111571. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892505 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prebiotics and Probiotics: Therapeutic Tools for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 5;24(19):14918. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914918. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of synbiotics on the cardiovascular risk factors in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver: a GRADE assessed systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 May 26;25(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03789-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40419987 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin/Glutaredoxin Systems and Gut Microbiota in NAFLD: Interplay, Mechanism, and Therapeutical Potential.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 28;12(9):1680. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091680. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37759983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of gut microbiome manipulation on glycemic indices in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a comprehensive umbrella review.Nutr Diabetes. 2024 May 10;14(1):25. doi: 10.1038/s41387-024-00281-7. Nutr Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38729941 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eslam M, Sarin SK, Wong VW, Fan JG, Kawaguchi T, Ahn SH, et al. . The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int. (2020) 14:889–919. 10.1007/s12072-020-10094-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

