Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with worse sexual function: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35958893
- PMCID: PMC9360519
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-22-190
Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with worse sexual function: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Several studies report that sexuality is often affected by inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). The aim of this meta-analysis was to investigate the association between IBD and sexual function.
Methods: A literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, and EMBASE databases (up to September 1, 2020). Scores of sexual functions with a standard deviation and odds ratio (OR) or relative risk (RR) with a 95% CI were used to analysis the association between IBD and sexual function.
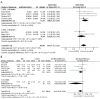
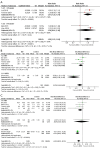
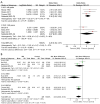
Results: Eleven studies with 7,018 male IBD cases and 1,803 female IBD cases were included in the meta-analysis. In male individuals, the pooled results revealed that IBD was significantly associated with impaired erectile function and poor sexual satisfaction (RR for erectile function =1.50, 95% CI: 1.22 to 1.84, P<0.0001; standard mean difference for sexual satisfaction =-0.24, 95% CI: -0.33 to -0.15, P<0.0001). And among female individuals, IBD had impact on most sub-domains of sexual function, except pains.
Conclusions: IBD is associated with worse sexual function. It has significant impact on erectile function and satisfaction for male individuals and has impact on most sub-domains of sexual function for female individuals.
Keywords: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); erectile function; satisfaction in sexual; sexual function; systematic review and meta-analysis.
2022 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-22-190/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Ananthakrishnan AN, Kaplan GG, Bernstein CN, et al. Lifestyle, behaviour, and environmental modification for the management of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: an International Organization for Study of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases consensus. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;7:666-78. 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00021-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
