MiRNA-148a inhibits cell growth and drug resistance by regulating WNT10a expression in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35958896
- PMCID: PMC9360522
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-22-464
MiRNA-148a inhibits cell growth and drug resistance by regulating WNT10a expression in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: We aimed to explore miR-148a exerts a tumor suppressor effect and arsenic trioxide (As2O3) sensitivity on renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Methods: We performed polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on 42 pairs of tumor and paracancerous samples collected from RCC patients to investigate the miR-148a expression; meanwhile, we analyzed the interplay between clinical indicators and miR-148a expression of RCC. Then, the influence of miR-148a overexpression on the functions of RCC cells were analyze using transwell migration assay, Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8), and cell wound healing assay. Furthermore, the ability of miR-148a to sensitize Caki-1 cells treated with As2O3 were detected using flow cytometry. Finally, the relevant mechanism of miR-148a on the downstream gene Wnt family member 10A (WNT10a) was explored by cell reverse method.
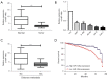
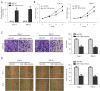
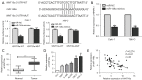
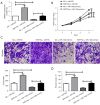
Results: The results from RCC patients indicated a significantly lower miR-148a level than adjacent tissues. The low miR-148a expression increased prevalence of distant metastasis and decreased survival rate compared to those with high expression in patients. In the RCC cell lines, the proliferation and metastasis ability of the miR-148a mimic group was remarkably lower than the miR-NC group. At the same time, it was verified that WNT10a was remarkably higher cell lines and RCC tissues; and negatively related to miR-148a expression. In addition, miR-148a mimics were found to remarkably reduce the protein expression of WNT10a. In the cell reverse experiment, overexpression of WNT10a was confirmed to offset the miR-148a mimics effect on metastasis and proliferation of RCC cells. In addition, an increase in relative apoptosis was detected in As2O3 treated with/without miR-148a mimics for 48 hours, and apoptosis was significantly reduced after transfection with WNT10a in the Caki-1 cell line and significantly reduced after combined treatment.
Conclusions: The study revealed that miR-148a is associated with distant metastases and leads to poor prognosis in RCC patients. Moreover, miR-148a inhibit the malignant progression and increase the sensitivity of RCC cells to As2O3 by regulating WNT10a.
Keywords: MiR-148a; WNT10a; arsenic trioxide; malignant progression; renal cell carcinoma.
2022 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-22-464/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MiRNA-206 inhibits proliferation of renal clear cell carcinoma by targeting ZEB2.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(18):7826-7834. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_18992. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31599407
-
miR-148a-3p inhibits the proliferation and migration of bladder cancer via regulating the expression of ROCK-1.PeerJ. 2022 Jan 26;10:e12724. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12724. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35127282 Free PMC article.
-
miR-488 inhibits cell growth and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma by targeting HMGN5.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Apr 18;11:2205-2216. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S156361. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. Retraction in: Onco Targets Ther. 2021 May 20;14:3351. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S318644. PMID: 29713189 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
CircUBAP2 Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma via Targeting miR-148a-3p/FOXK2 Pathway.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720925751. doi: 10.1177/0963689720925751. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32425115 Free PMC article.
-
miR-30c-2-3p suppresses the proliferation of human renal cell carcinoma cells by targeting TOP2A.Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2023 Oct 9;17(3):124-135. doi: 10.2478/abm-2023-0052. eCollection 2023 Jun. Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2023. PMID: 37818158 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role MicroRNA-135a in Suppressing Tumor Growth in Kidney Cancer Through the Regulation of Phosphoprotein Phosphatase2A and the Activation of the AKT and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 1;15(4):999-1008. doi: 10.7150/jca.90756. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38230208 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
