Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide ameliorated diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction in rats by regulating fibrosis and the NOS/ERK/JNK pathway
- PMID: 35958898
- PMCID: PMC9360518
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-22-428
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide ameliorated diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction in rats by regulating fibrosis and the NOS/ERK/JNK pathway
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction (DMED) is a frequent complication of diabetes mellitus (DM), with limited therapy at present. This study aimed to explore the role and mechanism of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide (GLP) on DMED.
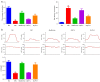
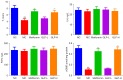
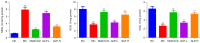
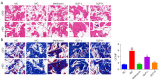
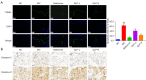
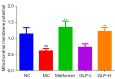
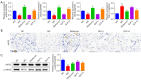
Methods: DMED was induced in the experimental rats [male 12-week-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats] by treatment with streptozotocin (60 mg/kg) and apomorphine (APO). Next, rats in the GLP low dose (GLP-L)/GLP high dose (GLP-H) groups were treated with GLP (100 or 400 mg/kg/d, respectively) for 8 weeks. Subsequently, erectile function was assessed by APO and electrostimulation of the cavernous nerve (CN). Serum or penile testosterone (T), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) contents were evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The levels of oxidative stress indicators in the corpus cavernosum (CC) were measured by corresponding kits, and histological changes in the CC were observed by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and Masson staining. Additionally, the apoptosis index, caspase-3, caspase-9, and eNOS expression, and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) were also detected. Furthermore, quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and western blot assays were conducted to determine the NOS, TGF-β1 mRNA expression, ERK1/2, eNOS, JNK phosphorylation, and arginase II protein expression.
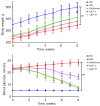
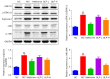
Results: The erectile function test revealed that erectile dysfunction (ED) was alleviated in the DMED rats following treatment with GLP. Moreover, GLP upregulated the T and cGMP content, improved the oxidative stress and histological injuries of CC, and also inhibited the apoptosis and MMP loss of penile tissues in DMED rats. Furthermore, GLP treatment enhanced the mRNA expression of NOS and TGF-β1 and suppressed the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, eNOS, and JNK, as well as the protein expression of arginase II in DMED rats.
Conclusions: GLP ameliorated DMED by repairing the CC pathological damage and upregulating NOS expression and ERK/JNK phosphorylation, indicating that GLP may be a candidate drug for DMED therapy.
Keywords: Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide (GLP); NOS/ERK/JNK pathway; corpus cavernosum (CC); diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction (DMED); fibrosis.
2022 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-22-428/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baicalein Alleviates Erectile Dysfunction Associated With Streptozotocin-Induced Type I Diabetes by Ameliorating Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Dysfunction, Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Fibrosis.J Sex Med. 2020 Aug;17(8):1434-1447. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2020.04.390. Epub 2020 Jun 23. J Sex Med. 2020. PMID: 32586748
-
Rapamycin Supplementation May Ameliorate Erectile Function in Rats With Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetes by Inducing Autophagy and Inhibiting Apoptosis, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Corporal Fibrosis.J Sex Med. 2018 Sep;15(9):1246-1259. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2018.07.013. J Sex Med. 2018. PMID: 30224017
-
NOX1/4 Inhibitor GKT-137831 Improves Erectile Function in Diabetic Rats by ROS Reduction and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Reconstitution.J Sex Med. 2021 Dec;18(12):1970-1983. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.09.007. Epub 2021 Oct 11. J Sex Med. 2021. PMID: 34649814
-
Therapeutic Challenges of Diabetes Mellitus-Related Erectile Dysfunction and The Potential Therapeutic Role of Medicinal Plants: A Narrative Review.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Apr 24;19:3209-3223. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S515403. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40297311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats.Sex Med Rev. 2020 Jan;8(1):114-121. doi: 10.1016/j.sxmr.2019.09.003. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Sex Med Rev. 2020. PMID: 31653438 Review.
Cited by
-
NLRP3 inhibitor combined with Yimusake improves erectile dysfunction in rats with diabetes mellitus through the attenuation of pyroptosis.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 27;10(19):e38626. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38626. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39391494 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling of human umbilical vein endothelial cells overexpressing CELF2 as diagnostic targets in diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Jul 7;12:1596534. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1596534. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40692719 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivities and industrial standardization status of Ganoderma lucidum: A comprehensive review.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 29;10(19):e36987. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36987. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39435114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Overexpressing RXFP1 via CRISPR Activation Ameliorate Erectile Dysfunction in Diabetic Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;12(1):171. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010171. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671033 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharides from natural resource: ameliorate type 2 diabetes mellitus via regulation of oxidative stress network.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 11;14:1184572. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1184572. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37497112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
