Jiedu-Yizhi Formula Alleviates Neuroinflammation in AD Rats by Modulating the Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 35958910
- PMCID: PMC9357688
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4023006
Jiedu-Yizhi Formula Alleviates Neuroinflammation in AD Rats by Modulating the Gut Microbiota
Abstract
Background: The Jiedu-Yizhi formula (JDYZF) is a Chinese herbal prescription used to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD). It was previously confirmed that JDYZF can inhibit the expression of pyroptosis-related proteins in the hippocampus of AD rats and inhibit gut inflammation in AD rats. Therefore, it is hypothesized that JDYZF has a regulatory effect on the gut microbiota.
Methods: In this study, an AD rat model was prepared by bilateral hippocampal injection of Aβ 25-35 and AD rats received high, medium, and low doses of JDYZF orally for 8 weeks. The body weights of the AD rats were observed to assess the effect of JDYZF. The 16S rRNA sequencing technique was used to study the regulation of the gut microbiota by JDYZF in AD rats. Immunohistochemical staining was used to observe the expression levels of Caspase-1 and Caspase-11 in the hippocampus.
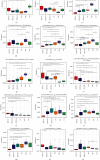
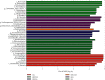
Results: JDYZF reduced body weight in AD rats, and this effect may be related to JDYZF regulating body-weight-related gut microbes. The 16S rRNA analysis showed that JDYZF increased the diversity of the gut microbiota in AD rats. At the phylum level, JDYZF increased the abundances of Bacteroidota and Actinobacteriota and decreased the abundances of Firmicutes, Campilobacterota, and Desulfobacterota. At the genus level, the abundances of Lactobacillus, Prevotella, Bacteroides, Christensenellaceae_R-7_group, Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group, and Blautia were increased and the abundances of Lachnospiraceae-NK4A136-group, Anaerobiospirillum, Turicibacter, Oscillibacter, Desulfovibrio, Helicobacter, and Intestinimonas were decreased. At the species level, the abundances of Lactobacillus johnsonii, Lactobacillus reuteri, and Lactobacillus faecis were increased and the abundances of Helicobacter rodentium and Ruminococcus_sp_N15.MGS-57 were decreased. Immunohistochemistry showed that JDYZF reduced the levels of Caspase-1- and Caspase-11-positive staining.
Conclusion: JDYZF has a regulatory effect on the gut microbiota of AD rats, which may represent the basis for the anti-inflammatory effect of JDYZF.
Copyright © 2022 Jiale Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association Report. 2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement . 2021;17(3):327–406. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

