Firm innovation activities and consumer brand loyalty: A path to business sustainability in Asia
- PMID: 35959050
- PMCID: PMC9358993
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.942048
Firm innovation activities and consumer brand loyalty: A path to business sustainability in Asia
Abstract
Background: In recent years, technological advancements have increased the importance of innovation activities. Therefore, firms invest millions of dollars in innovation activities to ensure long-term business sustainability. Similarly, consumer concerns have increased dramatically over the past years. Thus, brand loyalty has become a top priority for firms and consumers. In this background, this research examines how firms' innovation activities translate into consumer brand loyalty to assure business sustainability in Asian markets, particularly China, Pakistan, and Indonesia.
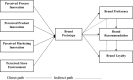
Objectives: This study's specific objectives are to comprehend the concept of firms' innovation activities and their effect on the brand prototype. Examine the effect of the brand prototype on global brand preference, recommendation, and loyalty among Asian consumers. Find out the impact of brand preference on brand recommendations and the influence of brand recommendations on brand loyalty among Asian consumers.
Materials and methods: A total of 814 consumers from Asian countries (China, Pakistan, and Indonesia) participated in this study, and structural equation modeling was used to analyze the data.
Results: The findings indicate that firms' innovation activities, such as processes, products, and store environment, positively influenced the brand prototype, thereby increasing consumer brand knowledge. Likewise, brand prototype contributes to developing brand preference, brand recommendation, and brand loyalty among Asian consumers. Lastly, consumer brand preference significantly influenced brand recommendation, which positively improves consumer brand loyalty in Asia.
Conclusion: This study concluded that Asian (Chinese, Pakistani, and Indonesian) consumers have favorable perceptions of firms' innovation activities (i.e., process, product, and store environment innovation), which influences their ability to develop brand prototypes to increase consumer brand knowledge. Similarly, brand prototype fosters brand preference, recommendation, and loyalty. Likewise, favorable brand preference encourages consumers to recommend the brand to others, strengthening brand loyalty. Thus, firms should invest in innovation activities to strengthen consumer brand loyalty in Asian markets. Consequently, this study may assist multinational corporations in increasing their business volumes and market shares in Asia.
Managerial recommendations: This study provides important managerial recommendations. The findings revealed that global managers can develop and implement several branding strategies for sustaining their businesses in the Asian environment.
Keywords: brand loyalty; brand preference; brand prototype; brand recommendation; innovation activities.
Copyright © 2022 Yi, Khan and Safeer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consumer Perceptions of Brand Localness and Globalness in Emerging Markets: A Cross-Cultural Context.Front Psychol. 2022 Jul 11;13:919020. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.919020. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35898987 Free PMC article.
-
The path of corporate low-carbon behavioral change: The impact of digital transformation on corporate green sports brand loyalty.J Environ Manage. 2025 Feb;374:124057. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2025.124057. Epub 2025 Jan 20. J Environ Manage. 2025. PMID: 39837146
-
Affect or cognition: which is more influencing older adult consumers' loyalty?Heliyon. 2018 Apr 20;4(4):e00610. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00610. eCollection 2018 Apr. Heliyon. 2018. PMID: 29862371 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of analyst attention on the firms' innovation paths from a life cycle perspective: Evidence from China.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 12;9(8):e18940. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18940. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37636392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of retailer innovativeness and food healthiness on store prestige, store trust and store loyalty.Food Res Int. 2019 Feb;116:724-730. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30717001 Review.
Cited by
-
Consumer Perceived Brand Innovativeness and Authenticity of Chinese Time-Honored Brand Restaurants: The Moderated Mediation Effect of Personal Traits.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023 Jul 4;16:2481-2498. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S407396. eCollection 2023. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2023. PMID: 37426387 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the innovation of time-honored brands from the perspective of dual ethical patterns.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 31;13:1041022. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1041022. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36798648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akgun A. E., Keskin H., Ayar H., Etlioglu T. (2017). Why companies go positive marketing innovations: a new theoretical prototype for 4ps of innovation. J. Bus. Econ. Finance 6 70–77. 10.17261/Pressacademia.2017.496 - DOI
-
- Aksoy H. (2017). How do innovation culture, marketing innovation and product innovation affect the market performance of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Technol. Soc. 51 133–141. 10.1016/j.techsoc.2017.08.005 - DOI
-
- Ardani W. (2019). Effect of product innovation and brand awareness on product purchase decisions of pt. unilever indonesia. Int. J. Educ. Inform. Technol. Others 2 151–165.
-
- Azar G., Ciabuschi F. (2017). Organizational innovation, technological innovation, and export performance: the effects of innovation radicalness and extensiveness. Int. Bus. Rev. 26 324–336. 10.1016/j.ibusrev.2016.09.002 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous