Neurosarcoidosis presenting as longitudinally extensive myelitis: Diagnostic assessment, differential diagnosis, and therapeutic approach
- PMID: 35959214
- PMCID: PMC9328025
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0231
Neurosarcoidosis presenting as longitudinally extensive myelitis: Diagnostic assessment, differential diagnosis, and therapeutic approach
Abstract
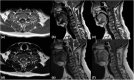
Neurosarcoidosis is an uncommon and multiform clinical entity. Its presentation as an isolated longitudinal extensive transverse myelitis (LETM) is rare and challenging to identify. We report a case of LETM in a 60-year-old patient with no significant systemic symptoms nor relevant medical history. The peculiar spinal magnetic resonance imaging finding characterized by a posterior and central canal subpial contrast enhancement, the so-called "trident sign," together with chest computed tomography scan and lymph node biopsy led to the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. We also discuss the main differential diagnoses of LETM and therapeutic options for sarcoidosis-related myelitis.
Keywords: longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis; neurosarcoidosis; sarcoidosis; treatment; trident sign.
© 2022 Alessandra Cicia et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tobin WO, Weinshenker BG, Lucchinetti CF. Longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2014;27:279–89. - PubMed
-
- Zajicek JP, Scolding NJ, Foster O, Rovaris M, Evanson J, Moseley IF, et al. Central nervous system sarcoidosis-diagnosis and management. QJM. 1999;92:103–17. - PubMed
-
- Hoitsma E, Faber CG, Drent M, Sharma OP. Neurosarcoidosis: a clinical dilemma. Lancet Neurol. 2004;3:397–407. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
